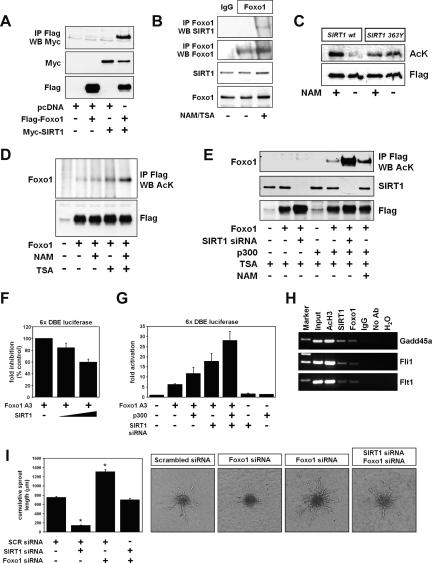
Figure 7.
SIRT1 interacts with Foxo1 in endothelial cells. (A) Interaction of SIRT1 with Foxo1. HUVECs were cotransfected with the Flag-tagged Foxo1 and the Myc-tagged SIRT1. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were lysed and Flag-tagged Foxo1 was immunoprecipitated. The immune complexes were assessed for the presence of SIRT1 (Myc) by Western blot analysis with antibodies to Myc. The amounts of Flag-Foxo1 and Myc-SIRT1 present in the cell extracts were analyzed with the respective antibodies. (B) Interaction of endogenous SIRT1 with Foxo1. HUVECs were left untreated or incubated with the SIRT1 inhibitor nicotinamide (NAM) and the class I/II HDAC inhibitor TSA for 2 h. Endogenous Foxo1 was immunoprecipitated with a goat polyclonal antibody to Foxo1 or a control preimmune goat serum (IgG). The immune complexes were assessed for the presence of SIRT1 by Western blot with an antibody to SIRT1. Amounts of endogenous Foxo1 and SIRT1 in the cell extracts were determined with antibodies to SIRT1 and Foxo1. (C) In vitro SIRT1 deacetylation assay. Acetylated Flag-tagged Foxo1 was immunoprecipitated using an antibody targeting the Flag epitope. The acetylated Foxo1 was incubated with immunoprecipitated wild-type SIRT1 (wt) or the deacetylase-defective SIRT1 mutant (H363Y) in the presence or absence of nicotinamide (NAM). Acetylation of Foxo1 was assessed by Western blot with antibodies to acetylated lysine. (D) HUVECs expressing Flag-tagged Foxo1 were incubated for 6 h in the absence or presence of the SIRT1 inhibitor nicotinamide (NAM), the class I/II HDAC inhibitor TSA, or combinations thereof. Flag-tagged Foxo1 was immunoprecipitated, and the acetylation of Foxo1 was assessed by Western blot with antibodies to acetylated lysine. (E) HUVECs were transfected with a SIRT1-specific siRNA or a scrambled control oligonucleotide and 24 h later with pcDNA, Flag-tagged Foxo1, p300, or combinations thereof. Endothelial cells were then incubated with TSA for 2 h. Flag-tagged Foxo1 was immunoprecipitated with antibodies targeting the Flag epitope. The acetylation of Foxo1 was assessed by Western blot analysis. (F) HUVECs were transiently transfected with expression plasmids encoding Foxo1 A3, SIRT1, and a forkhead-responsive element-driven luciferase reporter. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were lysed and cell extracts were assayed for luciferase expression. (G) HUVECs were transfected with a SIRT1-specific siRNA or a scrambled control siRNA and 24 h later with expression plasmids encoding pcDNA3, Foxo1 A3, p300, and a forkhead-responsive element-driven luciferase reporter. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were lysed and cell extracts were assayed for luciferase expression. (H) ChIP assays were performed with chromatin prepared from HUVECs incubated with nicotinamide (NAM) and TSA for 3 h. Chromatin was immunoprecipitated with mouse IgG or antibodies against SIRT1, Foxo1, or acetylated histone H3, and precipitated genomic DNA was analyzed by PCR using primers flanking conserved Foxo-binding sites in the promoter regions of the Gadd45a, Fli1, and Flt1 genes. (I) Representative images and statistical summary of a three-dimensional in vitro angiogenesis assay with collagen gel-embedded endothelial spheroids transfected with combinations of scrambled, SIRT1, and Foxo1 siRNAs. Cumulative sprout length was quantified after 24 h.