FIGURE 7.
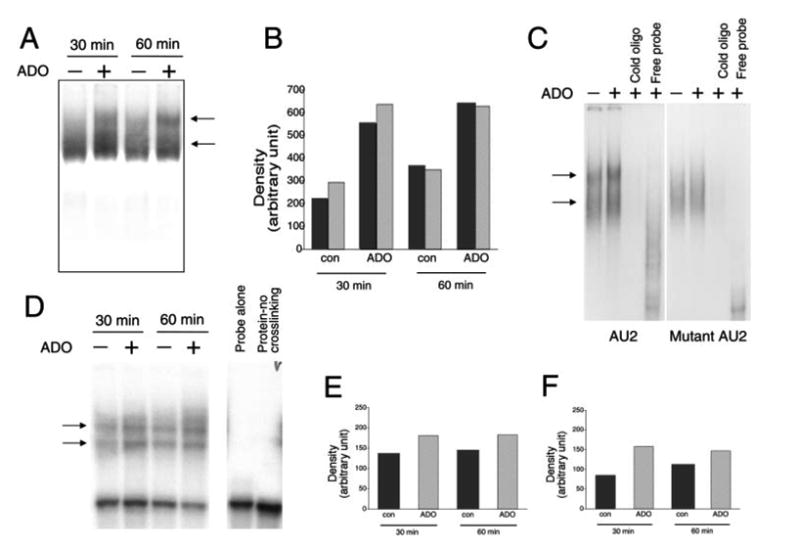
A, Adenosine (ADO) treatment of RAW 264.7 macrophages for 30 or 60 min increases RNA-protein complex formation between the AU2 region of the 3′-UTR of IL-10 mRNA and cellular components of RAW cells. Radiolabeled AU2 RNA probes were incubated with cytosolic fractions of RAW cells obtained at the end of the 30- or 60-min incubation period, complexes were separated by EMSA, and visualized using autoradiography. Two distinct complexes were observed in both untreated and treated cells. B, Densitometric analysis of intensities of the upper (■) and lower (
 ) complexes at 30 and 60 min following adenosine or control (con) treatment. C, Demonstration of the specificity of interactions between the AU2 region of the 3′-UTR of IL-10 mRNA and cellular fractions of RAW cells isolated 60 min after treatment with 100 μM adenosine. A 100× molar excess of cold AU2 oligonucleotide prevents formation of specific complexes in EMSA experiments (left panel). A mutated AU2 RNA probe lacking the GUAUUUAUU sequence forms a diffuse complex with cellular protein fractions of RAW cells as detected by EMSA (right panel). A 100× molar excess of cold mutated AU2 oligonucleotide prevents formation of this complex (right panel). D, UV cross-linking of cytosolic extracts from RAW 264.7 macrophages to an AU2 RNA probe results in formation of two specific complexes. Densitometric analysis indicates that adenosine treatment promotes formation of both the upper (E) and lower (F) complexes when measured using extracts taken 30 and 60 min after adenosine treatment of cells. Shown are representative results of a single experiment of three experiments with similar results.
) complexes at 30 and 60 min following adenosine or control (con) treatment. C, Demonstration of the specificity of interactions between the AU2 region of the 3′-UTR of IL-10 mRNA and cellular fractions of RAW cells isolated 60 min after treatment with 100 μM adenosine. A 100× molar excess of cold AU2 oligonucleotide prevents formation of specific complexes in EMSA experiments (left panel). A mutated AU2 RNA probe lacking the GUAUUUAUU sequence forms a diffuse complex with cellular protein fractions of RAW cells as detected by EMSA (right panel). A 100× molar excess of cold mutated AU2 oligonucleotide prevents formation of this complex (right panel). D, UV cross-linking of cytosolic extracts from RAW 264.7 macrophages to an AU2 RNA probe results in formation of two specific complexes. Densitometric analysis indicates that adenosine treatment promotes formation of both the upper (E) and lower (F) complexes when measured using extracts taken 30 and 60 min after adenosine treatment of cells. Shown are representative results of a single experiment of three experiments with similar results.
