Figure 3. 14-3-3 Binding Inhibits BZR1 Activity.
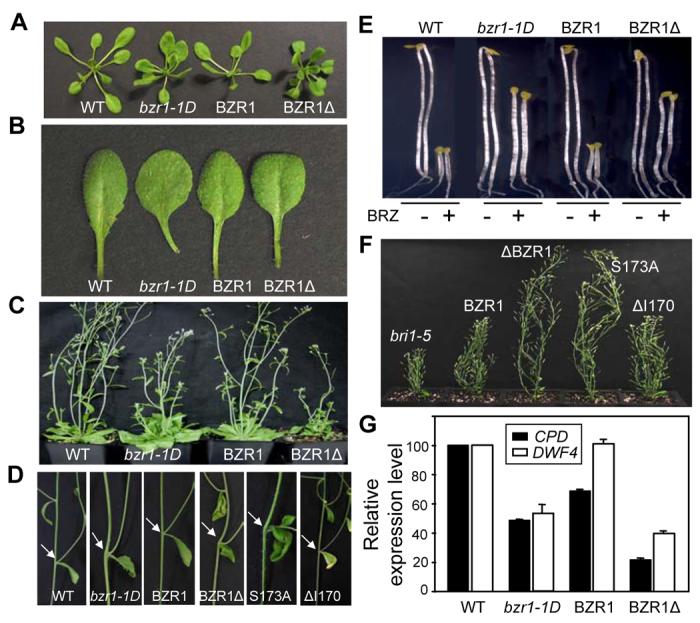
(A-D) Phenotypes of BZR1Δ and BZR1S173A transgenic plants compared with wild type Columbia (WT) and bzr1-1D. Three-week old plants (A) and leaves (B), five-week old plants (C) and bending of the stems at branch junction (pointed by arrows) (D).
(E) BZR1Δ and BZR1S173A mutations suppress BR-deficiency phenotypes. Seedlings were grown in the dark on MS medium with or without 2 μM BRZ for 4 days. Two representative seedlings for each treatment are shown.
(F) Mutations in BZR1 that reduce 14-3-3 binding suppress bri1-5 phenotype. Plants shown from left to right are bri1-5, bri1-5/BZR1-YFP, bri1-5/BZR1Δ-YFP, bri1-5/BZR1S173A-YFP and bri1-5/BZR1ΔI170-YFP.
(G) BR biosynthesis genes are down regulated in BZR1Δ plants. Expression levels of CPD and DWF4 genes were measured by Quantitative Real Time PCR. The data was normalized first to UBC and then to Col. Error bars are ± standard errors of mean.
