Figure. 3. LPA induces the expression levels of KLF5.
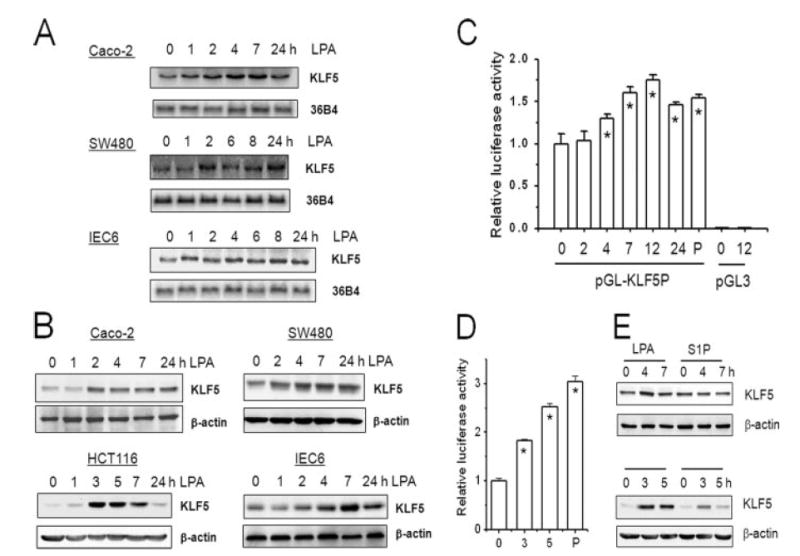
A, serum-starved Caco-2, SW480, and IEC6 cells were treated with 10 μM LPA for 0–24 h. Total RNA was isolated and the expression of KLF5 mRNA was detected by Northern blot hybridization using mouse KLF5 cDNA as probe. The amount of KLF5 mRNA was normalized to the expression levels of phosphoprotein 36B4 as a loading control (n = 3). B, serum-starved Caco-2, SW480, HCT116, and IEC6 cells were treated with 10 μM LPA for 0–24 h. 30 μg of whole cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and the amount of KLF5 protein was determined by Western blot using polyclonal anti-KLF5 antibody. Membranes were stripped and probed with an antibody against β-actin as a loading control. Representative Western blots from four separate experiments are shown. C, SW480cells were transiently transfected with pGL3 harboring KLF5 promoter, pGL-KLF5P, or pGL3. A Renilla luciferase control vector was co-transfected to normalize the transfection efficiency. 24 h post-transfection, cells were serum deprived for 24 h followed by treatment with LPA for the indicated times. As a control, PMA (P) was used as a positive agonist of the KLF5 promoter. Cell lysis and reporter assay were performed with Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay System. Three separate independent experiments were performed with at least 3 samples per condition. Results presented are mean ± S.E. *, p < 0.01 compared with untreated control. D, KLF5 promoter activity in HCT cells was determined as described above. *, p < 0.001. E, SW480 (upper panel) and HCT116 (lower panel) cells were treated with 10μM LPA or 1μM S1P. The amount of KLF5 protein was determined by Western blot as described earlier. Representatives of three independent experiments are shown.
