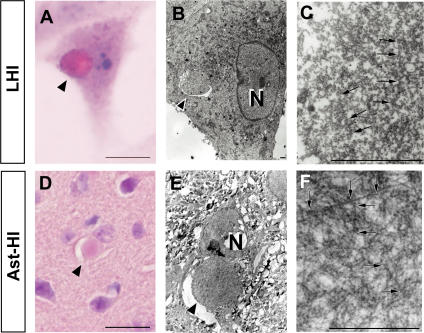
Figure 5. LHIs containing granule-coated fibrils are morphologically identical with Ast-HI from L84V transgenic mice.
(A–F) Comparison of a LHI induced by ER stress in an L84V SOD1-expressing SK-N-SH cell (A–C) and Ast-HI in the spinal cord of a transgenic L84V SOD1 mouse (D–F). (A) An eosinophilic LHI in the cytoplasm of the SK-N-SH cell expressing L84V SOD1 cell was induced by treatment with 1 µg/ml of tunicamycin for 24 h (scale bar = 20 µm). (B) Electron micrograph of a hyaline inclusion (arrow) obtained by the direct epoxy resin-embedding method after decolorization of the HE-stained section shown in (A). N, nucleus; ×3000 (scale bar = 1 µm). (C) At a high magnification, the inclusion is composed of granule-coated fibrils (arrows) approximately 15–25 nm in diameter and granular materials. ×16000 (scale bar = 1 µm). (D) An eosinophilic Ast-HI from a transgenic L84V SOD1 mouse. (E) Electron micrograph of an Ast-HI obtained by the direct epoxy resin-embedding method mentioned in (B). N, nucleus; ×2000 (scale bar = 1 µm). (F) Enlargement of (E). ×16000 (scale bar = 1 µm). Note that the fibrils observed in (C) and (F) are ultrastructually identical.