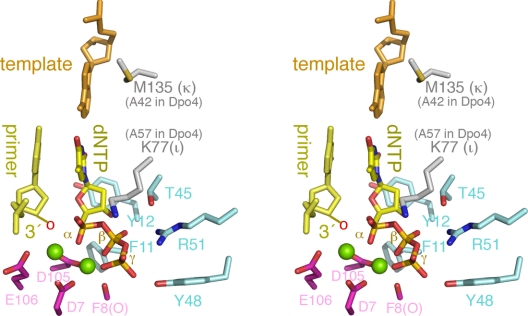
Fig. 4.
A composite active site of the Y-family polymerases in stereoview. The 3′-end nucleotide of the primer strand (pale yellow), the template nucleotide (orange), the incoming dNTP [yellow (C)/blue (N)/red (O)], the three catalytic carboxylates [magenta (C)/red (O)], the nearby carbonyl group [F8(O)] that coordinates one metal ion, and the conserved residues interacting with dNTP [light blue (C)/blue (N)/red (O)] are shown as sticks, and the two metal ions are shown as green spheres. These conserved residues are labeled according to Dpo4 for convenience. K77 of polι that stabilizes the incoming dNTP and M135 of polκ that stabilizes the template base are shown in gray/blue (N)/brown (S) sticks. These residues are replaced by Ala's in Dpo4. The 3′-OH group (indicated as a red “o”) is usually absent in the crystal structures for the purpose of capturing enzyme–substrate complexes.