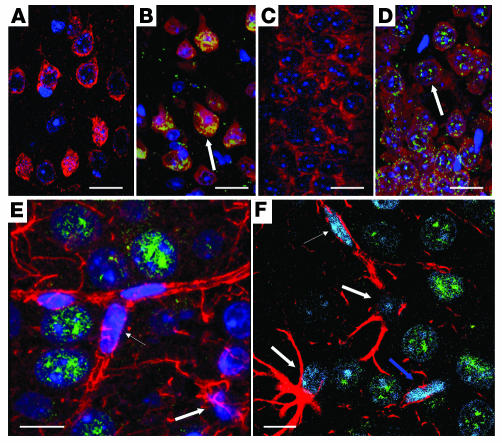
Figure 1. Neuronal localization of Gcdh expression (β-gal).
Motor cortex of WT (A) and Gcdh–/+ mouse (B) shows positive β-gal (green) staining colocalizes (yellow) with neurons (red) in layer V and VI of Gcdh–/+ mouse and not WT by immunofluorescence confocal microscopy. CA1 hippocampus from WT (C) and Gcdh–/+ mouse (D) shows positive β-gal staining for Gcdh–/+ mouse neurons only, similar to that found in motor cortex. Arrows indicate color change. (E) Average projection of 10 confocal slices through the CA1 hippocampus of a Gcdh–/+mouse shows no β-gal staining in endothelial cells (thin arrow) or astrocytes (red) (thick arrows). (F) A single slice through the CA1 hippocampus shows that nuclei associated with astrocytes (thick arrows) and endothelial cells (thin arrow) do not stain positive for β-gal while large nuclei of neurons are positively stained. β-Gal labeling is nuclear due to nuclear localizing sequence; see Methods. (A–D) β-Gal, green; NeuN, red; colocalization β-gal and NeuN, yellow; and DAPI, blue. Scale bars: 10 μm. (E and F) β-Gal, green; GFAP, red; and DAPI, blue. Scale bars: 10 μm.