Figure 1. Palladin interacts with SPIN90 and Src.
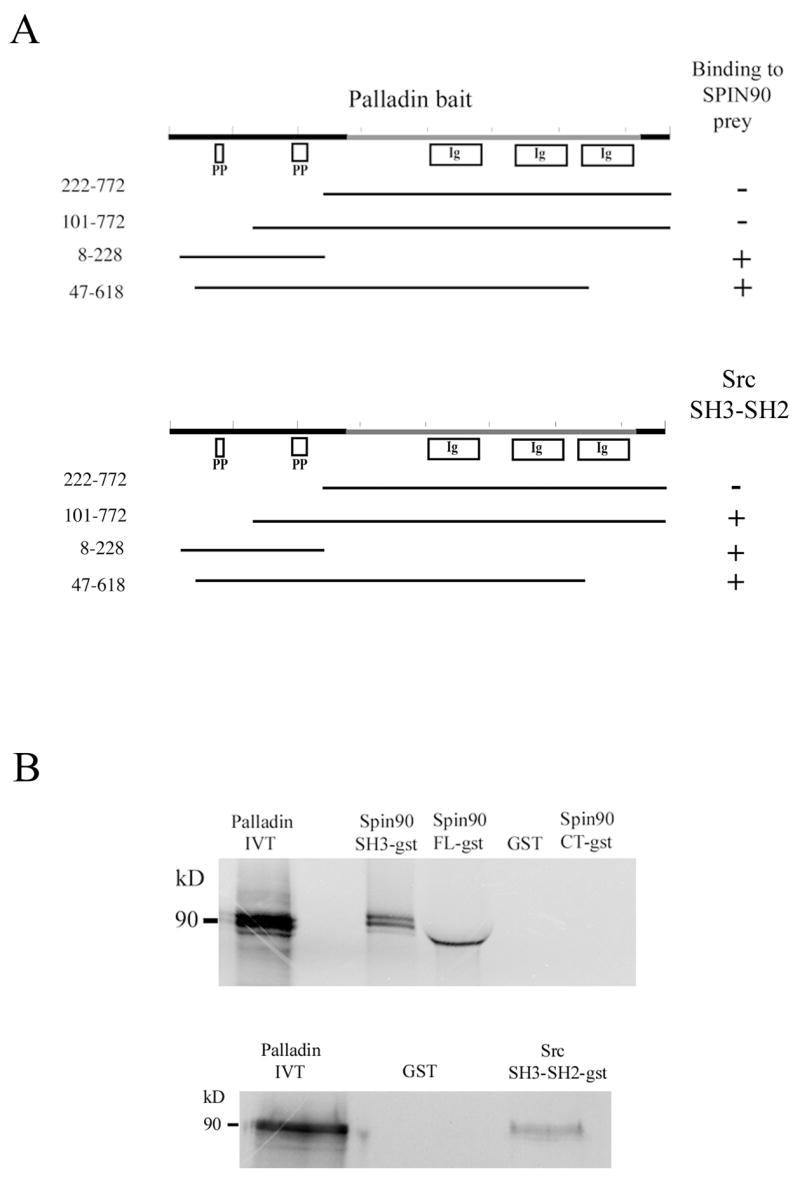
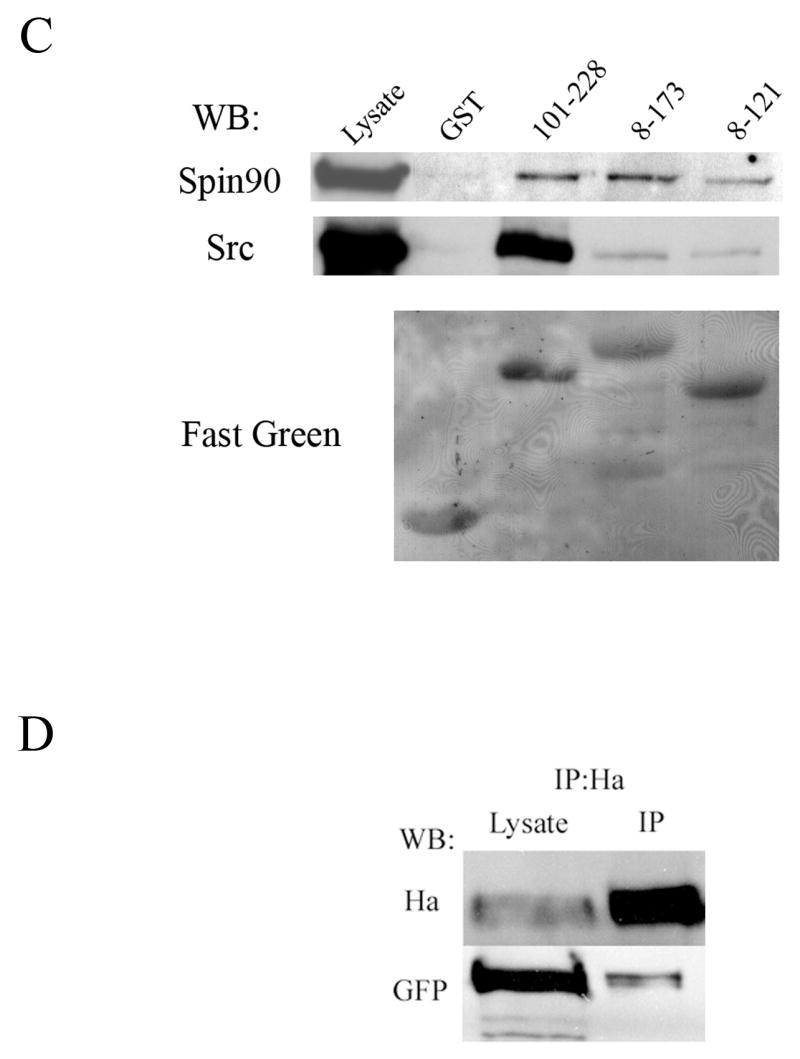
(A) Yeast-two hybrid analysis. Yeast cells were cotransformed with various palladin fragments in bait vector and either full length SPIN90 or Src SH3-SH2 in prey vector. Interaction was monitored by scoring growth on plates lacking histidine and by a filter based β-galactosidase assay. + = positive reaction, − = negative reaction. A scheme of the domains palladin 3Ig isoform is shown on top. The poly-proline (PP) regions are necessary for the interaction with SPIN90 and Src. Ig = immunoglobulin domain. (B) Affinity precipitation assay. In vitro translated (IVT) 35S-labeled palladin 8–772 was allowed to bind GST-SPIN90 and GST-Src constructs coupled to glutathione-Sepharose beads. The panel is an autoradiograph showing the material eluted from beads. The SH3-domain of SPIN90 and SH3-SH2 domain of Src is sufficient in mediating the interaction. GST-FL-SPIN90 and IVT palladin have a similar molecular weight, which explains the slightly differential mobility of IVT protein in the gel. (C). Interaction between palladin poly-proline sequences, SPIN90 and Src. HEK293 cells were transfected with a HA-tagged full length SPIN90 or with wild type Src construct. The cleared lysates were allowed to bind GST (lane 2) or GST-palladin constructs containing the indicated residues on glutathione-Sepharose beads. Bound proteins were resolved in a 10% SDS-PAGE gel and detected either with a SPIN90 or a Src antibody. SPIN90 binding does not show marked preference between the poly-proline sequences, whereas Src binds preferably to the sequence contained within the 101–228 construct. Lane 1 shows immunoblotting of the cell lysates and bottom panel shows Fast Green staining of the membrane to demonstrate the equal loading of GST constructs. (D) Coimmunoprecipitation. COS-7 cells were co-transfected with HA-tagged palladin and GFP-tagged SPIN90. The cleared lysate was immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody and the precipitate was blotted with anti-HA and anti-GFP antibody. The GFP-tagged protein is detected in the precipitate thus verifying the interaction.
