Fig. 7.
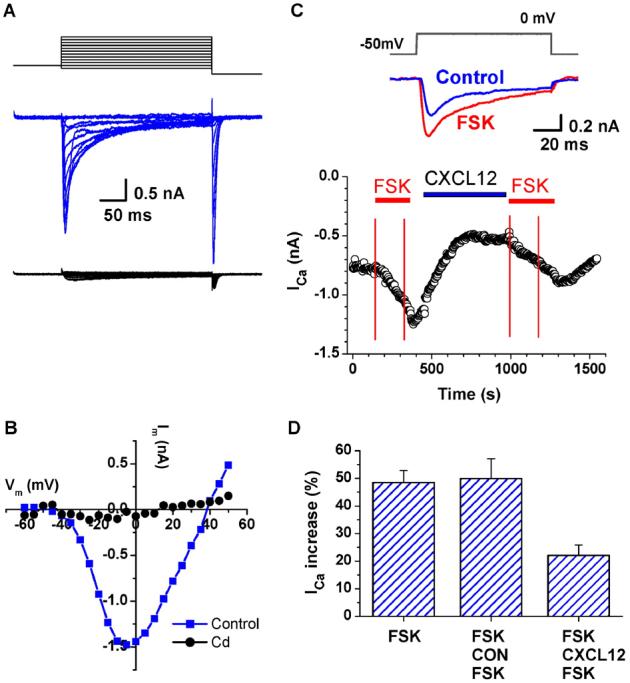
CXCL12 modulates forskolin (FSK)-induced Ca2+ channel activation in CM. Whole-cell recording of inward Ca2+ currents from isolated rat ventricular CM with 1 mM CaCl2 in the bath solution. L-type Ca2+ currents were activated with the step voltage clamp protocol shown in the top panel. Currents were mostly blocked by Cd (0.1 mM, lower panel in red) (A). I-V plot of the L-type Ca2+ current in control conditions (blue) and in 0.1 mM Cd (red) (B). Time course of Ca2+ current in response to the application of FSK (1 μm) and CXCL12 (100 ng/ml). The top panel illustrates the voltage protocol and typical current traces under each condition. The inward Ca2+ currents were activated by a repeating voltage step from −50 mV to 0 mV. Inward current values were measured at the inward peak. The bottom panel illustrates the relative changes of peak currents during 3-min applications of FSK (1 μM) indicated by the red horizontal lines. CM were exposed for approximately 5 min to either CXCL12 (FSK-CXCL12-FSK) or diluent (FSK-CON-FSK), as indicated by the blue horizontal line, before the second FSK application (C). Summary of the CXCL12 attenuation of the FSK-induced Ca2+ current stimulations is shown (n=5) (D).
