Fig. 2.
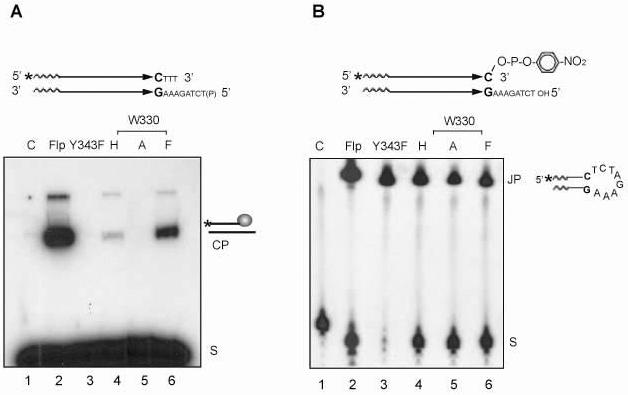
Strand cleavage and joining by Flp mutants altered at Trp-330. A. In the strand cleavage substrate, schematically diagrammed at the top, the parallel arrows ending in the CG bp represent the Flp binding element. The asterisk denotes the 32P label at the 5' end. Strand cleavage by Flp would result in the loss of the trinucleotide 5'HOTTT3' by diffusion. The 5'-hydroxyl group of the bottom strand was blocked by phosphorylation. The substrate (S) and the cleaved product covalently linked to Flp (CP) were separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. B. The 5' end-labeled substrate contained a p-nitrophenolate moiety linked to the 3'-phosphate end. The joined product (JP) was fractionated away from the substrate (S) by electrophoresis in a denaturing polyacrylamide gel. Note that some intermolecular joining reaction could also occur under the reaction conditions. In the denaturing gel, this product was not distinguishable from the hairpin product diagrammed. Reactions in A and B were carried out at 30°C for 30min. The lanes marked ‘C’ here and in other reactions (Fig. 3-6 and Fig. 8) are ‘substrate-alone’ controls.
