Fig. 9.
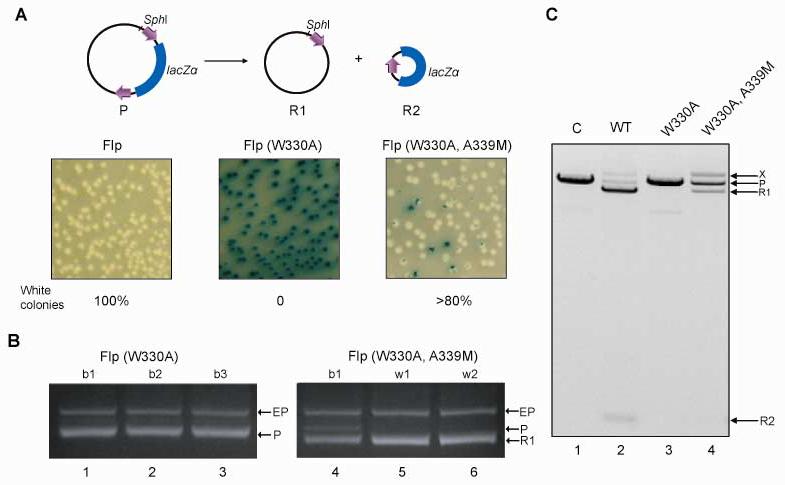
Rescue of Flp(W330A) in recombination by a second site mutation A339M. The excision assay for Flp recombination in E. coli is schematically depicted at the top. A. The recombination event causing deletion of the lacZα cassette is declared by the switch in colony color from blue to white on X-gal plates. The product R2 is lost from the population for lack of a replication origin. B. Resident plasmids from randomly picked blue (b) and white (w) colonies were isolated, digested with SphI, and fractionated by electrophoresis in 1% agarose gels. The expression plasmids, the parent reporter plasmid and the larger of two recombinant products derived from it, all in their linear forms, are indicated by ‘EP’, ‘P’ and ‘R1’, respectively. C. Following in vitro recombination, the extracted DNA was digested with SphI, and subjected to electrophoresis as under A. ‘P’ refers to the linearized substrate, and ‘R1’ to the linear form of the larger deletion product. The smaller deletion circle is denoted by ‘R2’. The band above R1 in the Flp(W330A, A339M) reaction ‘X’ was due to integration of the deletion circle into P via an intermolecular recombination event.
