Figure 1.
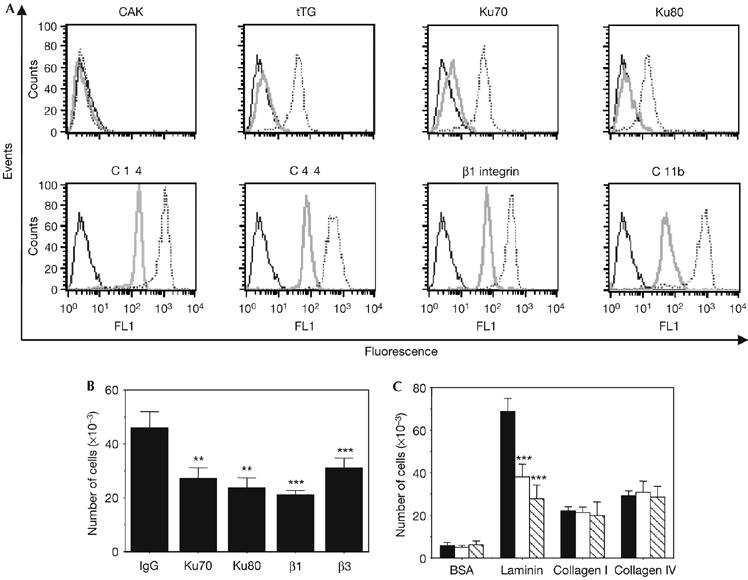
Monocyte differentiation is associated with expression of Ku on the cell surface, which contributes to the regulation of the cell migration on fibronectin. (A) Cell-surface expression of the indicated antigens was analysed by flow cytometry in resting (grey) or differentiated (18 h; dashed) monocytes. The results obtained for isotype-matched controls in differentiated monocytes are shown (black) and were identical between resting and activated monocytes. (B) Monocytes were treated overnight with 10 ng/ml of M-CSF and then placed into the upper chambers of Transwells, undercoated with fibronectin. The cells were pre-incubated for 1 h with the indicated antibodies before being added to fibronectin-coated wells. The means of three separate experiments carried out in duplicate are shown. **Statistically significant by Student's t-test, P<0.01 relative to control; *** statistically significant by Student's t-test, P<0.001 relative to control. (C) Similar experiments were carried out with inserts undercoated with the indicated substrates. Cells were pre-incubated with control Ig (black), Ku70 (white) or Ku80 (hatched) antibodies. The means of three separate experiments carried out in duplicate are shown. Statistically significant by Student's t-test, ***P<0.001 relative to control. BSA, bovine serum albumin; CAK, cyclin dependent kinase activating kinase; FL1-H, fluorescence pulse 1-height; Ig, immunoglobulin; M-CSF, monocyte colony-stimulating factor; tTG, tissue transglutaminase.
