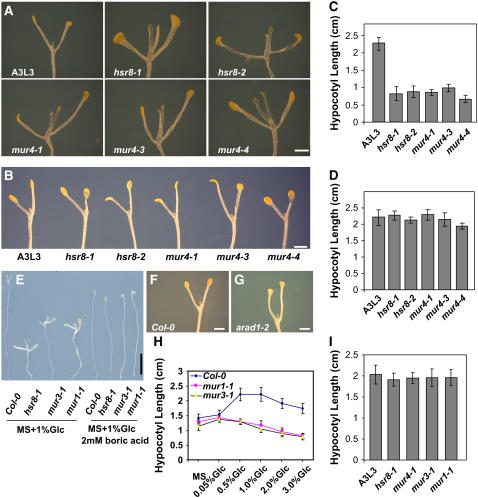
Figure 5.
Dark Development Phenotypes of Cell Wall Biosynthetic Mutants.
(A) Dark development phenotypes of 14-d-old wild-type Col-0, mur4, and hsr8 alleles grown on MS medium supplemented with 1% glucose. All hsr8 alleles exhibit increased dark development compared with the wild type.
(B) Dark development phenotypes of 14-d-old wild-type Col-0 and hsr8 alleles grown on MS medium supplemented with 1% glucose and 30 mM l-arabinose. The increased dark development phenotypes of hsr8 mutants in response to glucose were restored to wild-type levels by exogenous l-arabinose.
(C) Hypocotyl lengths of 14-d-old dark-grown seedlings of the wild type and hsr8 mutants grown on MS medium supplemented with 1% glucose.
(D) Hypocotyl lengths of 14-d-old dark-grown seedlings of the wild type and hsr8 mutants grown on MS medium supplemented with 1% glucose and 30 mM l-arabinose. The reduced hypocotyl elongation of hsr8 mutants was rescued by l-arabinose.
(E) Dark development phenotypes of 14-d-old wild type Col-0, hsr8-1, mur3-1, and mur1-1 alleles grown on MS medium supplemented with 1% glucose (left) or with 1% glucose + 2 mM boric acid (right). Dark development and hypocotyl length of hsr8-1, mur4-1, mur3-1, and mur1-1 were restored to wild-type levels (see [I]).
(F) and (G) Dark development phenotypes of 14-d-old wild type Col-0 (F) and arad1-2 (G) alleles grown on MS medium supplemented with 1% glucose.
(H) Hypocotyl lengths of 14-d-old dark-grown seedlings of Col-0, mur1-1, and mur3-1 grown on MS medium supplemented with different glucose concentrations.
(I) Hypocotyl lengths of 14-d-old dark-grown seedlings of Col-0, mur1-1, and mur3-1 grown on MS medium supplemented with 1% glucose + 2 mM boric acid.
Error bars represent sd (n > 30). Bars = 0.5 mm in (E) and 1 mm in (A), (B), (F), and (G).