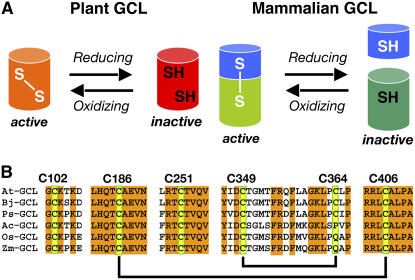
Figure 1.
Thiol-Based Changes in GCL.
(A) Comparison of plant and mammalian GCL responses to redox environment. The plant GCLs are regulated by intramolecular disulfide bonds. The mammalian GCL are regulated by intermolecular disulfided bonds formed between catalytic (green) and regulatory (blue) subunits.
(B) Cys residues in the plant GCL. Shown amino acid sequences correspond to regions around the Cys residues in the GCL from Arabidopsis (At GCL; NP194041), B. juncea (Bj GCL; EMB:CAD91713.1), Pisum sativum (Ps GCL; GB:AAF22127.1), Allium cepa (Ac GCL; GB:AAL61610.1), Oryza sativa (Os GCL; EMB:CAD48599.3), and Zea mays (Zm GCL; EMB:CAC83005.1). Yellow boxes highlight Cys residues in At GCL. Amino acid numbering corresponds to At GCL. Disulfide bonds found in At GCL and Bj GCL are indicated by black lines.