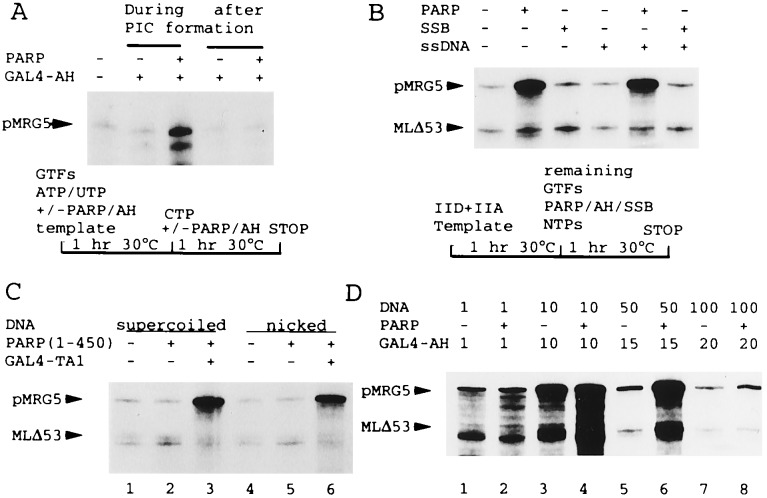
Figure 3.
(A) A combination of PARP and GAL4-AH is inactive when added after PIC formation. GAL4-AH and PARP (Mono S fraction) were added, as indicated, either during a 1-h preincubation of GTFs, ATP, and UTP, and 100 ng of pMRG5 template (lanes 3 and 4) or during the following 1-h incubation under standard transcription conditions with added CTP. A schematic protocol is shown below. (B) PARP and GAL4-AH function when added after formation of a TFIID-TFIIA-DNA complex. After preincubation of DNA, TFIID, and TFIIA according to the protocol indicated, transcription was initiated by addition of other GTFs, NTPs, GAL4-AH (all lanes) along with PARP (Mono S fraction), E. coli single-stranded-DNA-binding protein (SSB) (200 ng), or a 60-bp single-stranded DNA promoter-derived oligonucleotide (ssDNA, present at twice the concentration of the template) as indicated. (C) PARP does not act through binding to nicked templates. Standard transcription reactions contained supercoiled (lanes 1–3) or nicked (lanes 4–6) DNA templates and GAL4-TA1 and purified recombinant PARP (500 ng of a deletion protein containing amino acids 1–450) as indicated. (D) PARP function is strictly DNA concentration-dependent. Standard transcription reactions contained variable amounts of template DNA (indicated in ng), GAL4-AH (units indicated, with 10 units the standard amount), and PARP (natural Mono S fraction) as indicated.