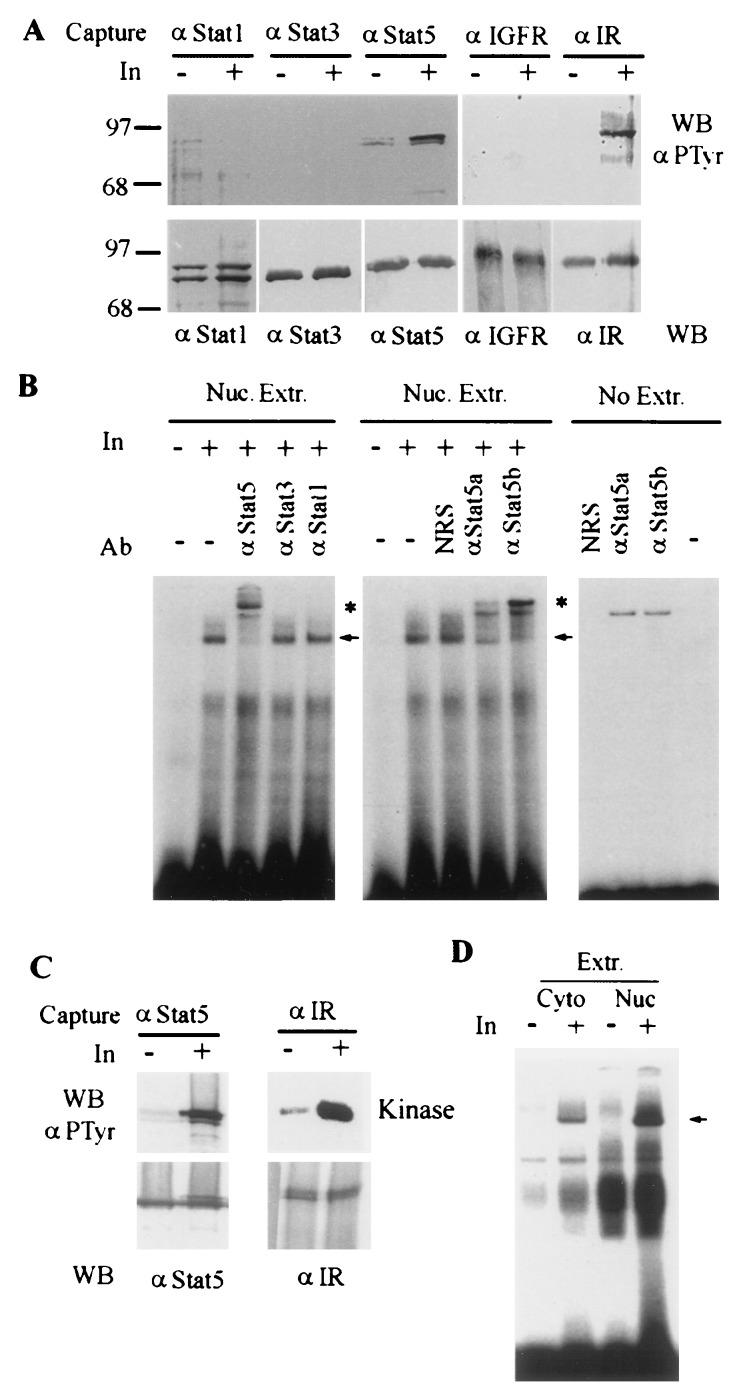
Figure 4.
Insulin stimulates Stat5 tyrosine phosphorylation and DNA binding activity in perfused liver. (A) Stat5 is tyrosine phosphorylated in mouse liver perfused with insulin. The livers were perfused with 10 ml Hanks solution containing either 1 mM Na3VO4 or 1 mM Na3VO4 plus insulin (50 nM). After 10 min, the liver lysates were prepared. Three milligrams of protein of each lysate was immunoprecipitated with antibodies against Stat1, Stat3, Stat5, IR, or IGF1 receptor and then divided into two parts, one part for Western blotting to detect tyrosine phosphorylation (Upper) and the other for assessing protein amount (Lower). (B) Insulin stimulates Stat5 DNA-binding activity. Nuclear proteins were extracted from the perfused mouse liver and subjected to EMSA using a 32P-labeled double-stranded oligonucleotide probe that contained a MGF/Stat5 binding site from the β-casein promoter (PIE) (29). The Stat-specific antibodies were used for supershift assay. The nonspecific supershift was determined in the absence of nuclear extract. (C) Stat5 is tyrosine phosphorylated in mouse liver perfused with insulin in the absence of sodium vanadate. Conditions were the same as in A except sodium vanadate was not added in the perfusion buffer, and 6 mg of total protein of each lysate was used for analysis. (D) Insulin stimulates Stat5 DNA binding in the absence of sodium vanadate. Frozen pieces of the mouse livers perfused as described in C were thawed and cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were prepared. Stat5 DNA-binding activity in these extracts (30 μg) was assessed similarly using PIE probe. Arrows indicate the specific insulin-inducible complexes; asterisks indicate supershifted Stat5-containing complexes.