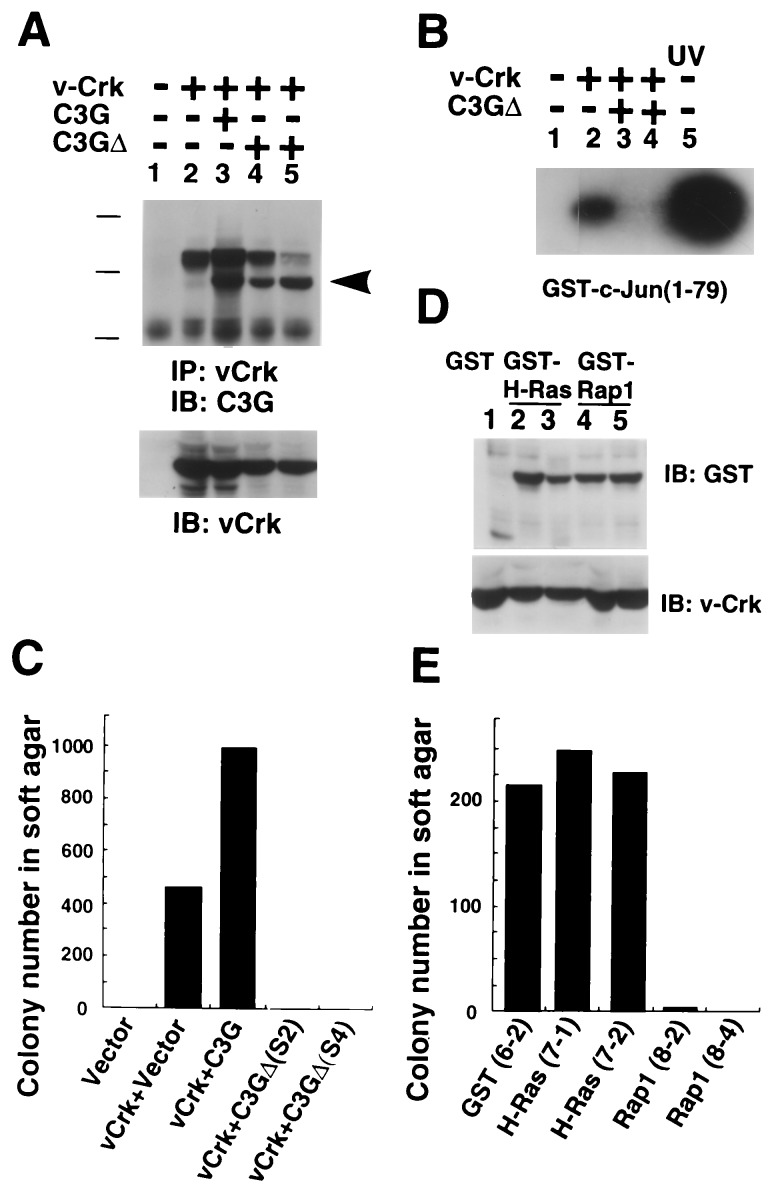
Figure 3.
Involvement of guanine nucleotide exchange domain of C3G in v-Crk induced JNK activation and transformation. (A) Two v-Crk NIH 3T3-derived cell lines stably expressing C3GΔ, lacking CDC25 homology region, were established (clones S2 and S4). (Upper) The association of C3GΔ and v-Crk was detected by immunoprecipitation. Arrowhead indicates the position of C3GΔ. The proteins expressed in each cell line are indicated at the top. v-Crk was immunoprecipitated from lysate containing 500 μg of total protein by anti-gag antibody (3C2) and resultant blot was probed with anti-C3G antibody. Bars shows the molecular mass 200, 118, and 86 kDa. (Lower) The levels of v-Crk were detected by immunoblotting with anti-gag antibody, using 20 μg of protein in total cell lysate per lane. (B) JNK activity of each cell line was determined by in vitro kinase assay as described in Fig. 1. The proteins expressed in each cell line are indicated at the top. (C) Anchorage-independent growth of NIH 3T3 cell lines expressing v-Crk and C3GΔ. (D) Establishment of v-Crk NIH 3T3 cell line stably expressed GST (lane 1, clone 6-2), GST-H-Ras (lanes 2 and 3, clones 7-1 and 7-2, and GST-Rap-1 (lanes 4 and 5, clone 8-2 and 8-4). Expression levels of GST fusion proteins and v-Crk were confirmed by anti-GST antibody and anti-gag antibody, respectively. (E) Anchorage-independent growth of v-Crk NIH 3T3 cells expressing GST, GST-H-Ras, and GST-Rap-1.