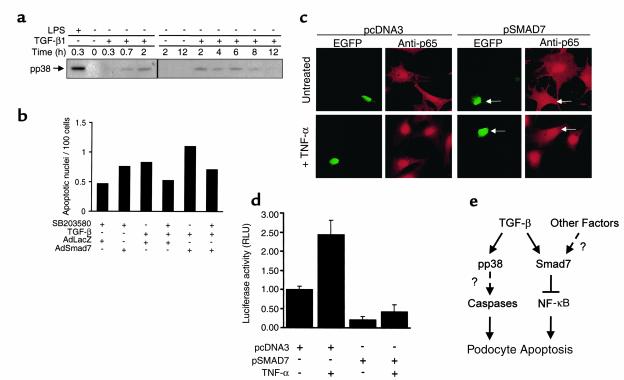
Figure 6.
(a) Immunoblot demonstrates levels of phosphorylated p38 MAP kinase (pp38) in podocytes treated with LPS as positive control or TGF-β1 for various time intervals. (b) Histogram shows the normalized average numbers of apoptotic cells as detected by TUNEL assay per hpf (in 50 hpf total) from a representative experiment. Podocyte cultures were infected with AdLacZ or AdSmad7 adenoviral vectors and left untreated or treated with TGF-β in the absence or presence of p38 MAP kinase inhibitor SB203580. Results were normalized for total cell density. (c) Detection of the NF-κB p65-subunit (anti-p65) by indirect immunofluorescence in podocytes transiently cotransfected with green fluorescent protein expression plasmid pEGFP together with either empty control vector pcDNA3 or Smad7 expression vector pSmad7. Cells were either left untreated or treated with TNF-α for 30 minutes. Arrows indicate GFP and anti-p65 signals in pEGFP/pSmad7-cotransfected cells. (d) Bar graph showing normalized luciferase activity (RLU) mediated by the NF-κB–responsive reporter gene construct NF-κB-luc in podocytes cotransfected with pcDNA3 empty control or pSmad7 expression vectors. Cells were either left untreated or stimulated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) after transfection. (e) Schematic demonstration of a new working model for proapoptotic signaling pathways induced by TGF-β and Smad7.