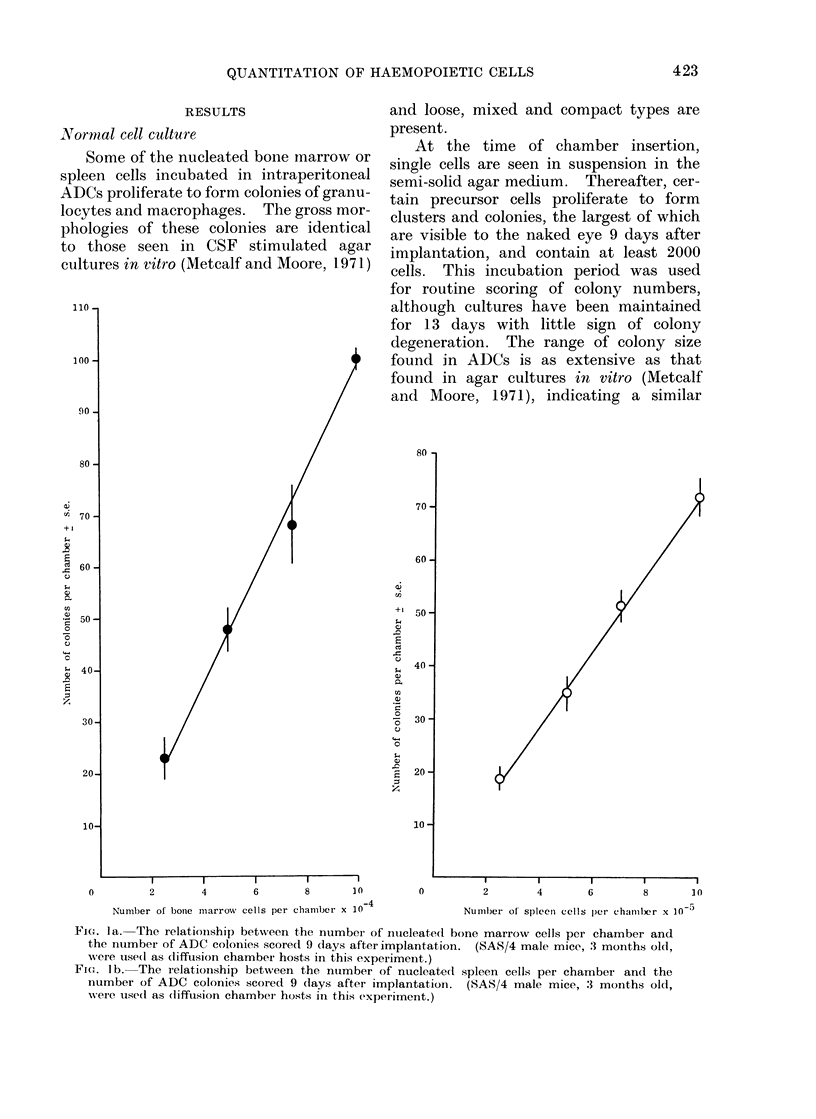
Abstract
The conventional diffusion chamber (CDC) as described by Benestad (1970) had been modified to assay the colony forming capacity of RFM bone marrow and spleen cells in agar diffusion chambers (ADCs). The colonies are morphologically identical to those formed by the CFUc in agar culture in vitro and have an incidence of approximately 1 in 103 normal nucleated bone marrow cells, and 1 in 104 nucleated spleen cells. Comparison of the growth of normal bone marrow cells in CDCs and in ADCs suggests that cell proliferation in diffusion chambers may result from the same precursor cell as detected by colony formation in agar culture in vitro. This proposal is supported by the suicide of approximately 46% of the ADC colony precursor cells following incubation with 3H-labelled thymidine.
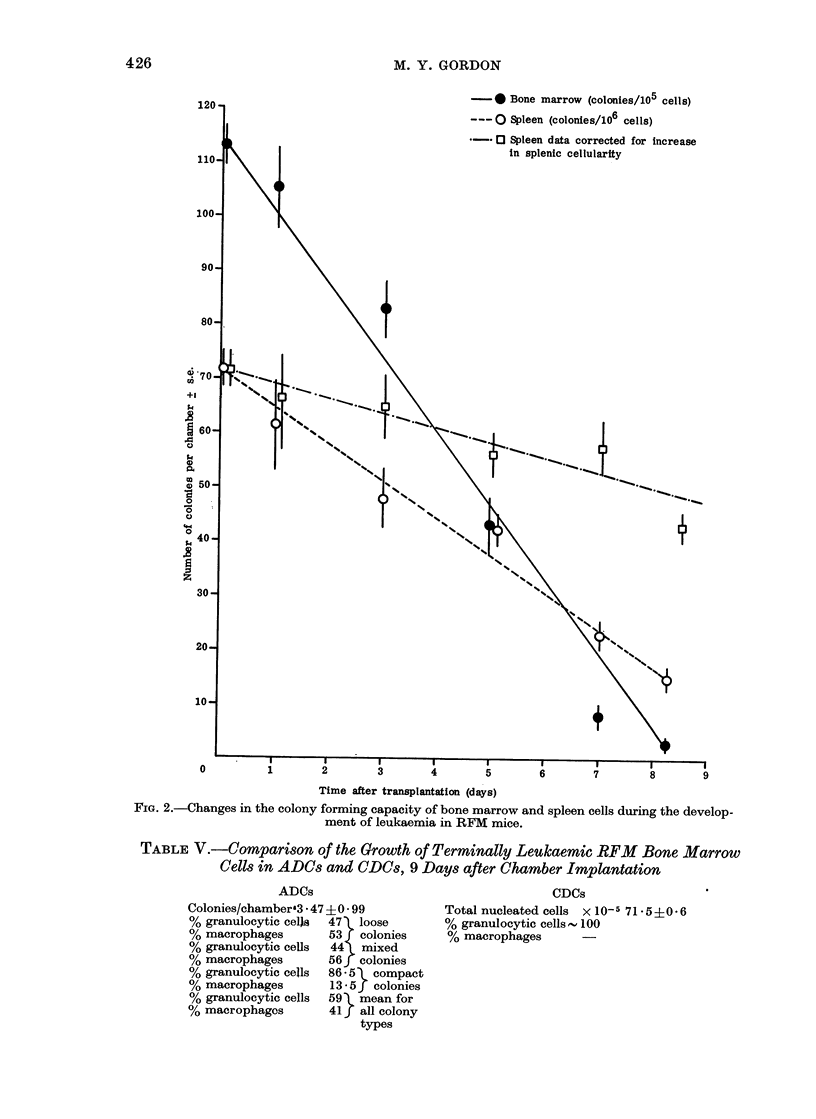
Colony formation by haemopoietic cells taken from leukaemic mice appears to be due to the proliferation of a remaining normal cell population alone, while the leukaemic cells in the inoculum form a background of uniformly distributed blast cells. In the case of leukaemic cell culture, there are differences in the results from CDCs and ADCs, and data from colonies in leukaemic ADC cultures are similar to those from normal ADC colonies. These comparisons imply that the ADC technique may be used to monitor the functional capacity of normal bone marrow, by its ability to form colonies, during the development of leukaemia. A humoral effect of a leukaemic environment on the growth of normal bone marrow cells in ADCs has also been detected.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benestad H. B. Formation of granulocytes and macrophages in diffusion chamber cultures of mouse blood leucocytes. Scand J Haematol. 1970;7(4):279–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1970.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyum A., Boecker W., Carsten A. L., Cronkite E. P. Proliferation of human bone marrow cells in diffusion chambers implanted into normal or irradiated mice. Blood. 1972 Aug;40(2):163–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyum A., Borgstrom R. The concentration of granulocytic stem cells in mouse bone marrow, determined with diffusion chamber technique. Scand J Haematol. 1970;7(5):294–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyum A., Carsten A. L., Laerum O. D., Cronkite E. P. Kinetics of cell proliferation of murine bone marrow cells cultured in diffusion chambers: effect of hypoxia, bleeding, erythropoietin injections, polycythemia, and irradiation of the host. Blood. 1972 Aug;40(2):174–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. R., Metcalf D. The growth of mouse bone marrow cells in vitro. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Jun;44(3):287–299. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breivik H., Benestad H. B., Boyum A. Diffusion chamber and spleen colony assay of murine haematopoietic stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Aug;78(1):65–72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicke K. A., Platenburg M. G., van Bekkum D. W. Colony formation in agar: in vitro assay for haemopoietic stem cells. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1971 Sep;4(5):463–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1971.tb01554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M. Y., Coggle J. E. CFU-C yields from the haemopoietic tissues of normal and leukaemic RFM mice. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1974 Jan;7(1):61–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1974.tb00399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Senn J. S., Till J. E., McCulloch E. A. Colony formation by normal and leukemic human marrow cells in culture: effect of conditioned medium from human leukocytes. Blood. 1971 Jan;37(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. Effect of thymidine suiciding on colony formation in vitro by mouse hematopoietic cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Feb;139(2):511–514. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. Human leukaemia: recent tissue culture studies on the nature of myeloid leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 1973 Mar;27(3):191–202. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1973.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The nature of leukaemia: neoplasm or disorder of haemopoietic regulation? Med J Aust. 1971 Oct 9;2(15):739–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike B. L., Robinson W. A. Human bone marrow colony growth in agar-gel. J Cell Physiol. 1970 Aug;76(1):77–84. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040760111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The cloning of normal "mast" cells in tissue culture. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Dec;66(3):319–324. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein A. S., Trobaugh F. E., Jr Ultrastructure of presumptive hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 1973 Jul;42(1):61–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TILL J. E., McCULLOCH E. A. A direct measurement of the radiation sensitivity of normal mouse bone marrow cells. Radiat Res. 1961 Feb;14:213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bekkum D. W., van Noord M. J., Maat B., Dicke K. A. Attempts at identification of hemopoietic stem cell in mouse. Blood. 1971 Nov;38(5):547–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


