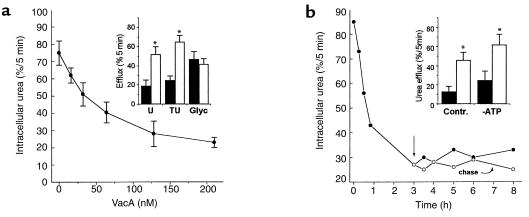
Figure 4.
Dose response, selectivity, kinetics, and energy dependence of VacA-induced permeabilization of the plasma membrane of AGS cells. (a) Nonpolarized AGS cells were intoxicated with increasing concentration of VacA, and the rate of urea efflux was determined after equilibration. Inset: AGS cells were treated as above with VacA (50 nM), washed, and incubated with PBS-BSA at 4°C supplemented with 45 μM [14C]urea (U), [14C]thiourea (TU), or [3H]glycerol (Glyc). The amount of released radioactivity was determined after 5 minutes. Data are the mean of three to four experiments run in duplicate ± SE. (b) Nonpolarized AGS cells were incubated with 125 nM of activated VacA for the indicated time intervals and then washed and assayed for [14C]urea release. The arrow indicates washing out of toxin before further incubation, in parallel samples (chase). Inset: AGS cells were or were not incubated under ATP-depleting conditions (see Methods) and treated for 3 hours with activated VacA (open bars) or left untreated (filled bars). The rate of urea efflux was then determined. The mean of three experiments ± SE is reported. *The quantities compared are statistically different (Student’s t test; P < 0.05). Contr., control.