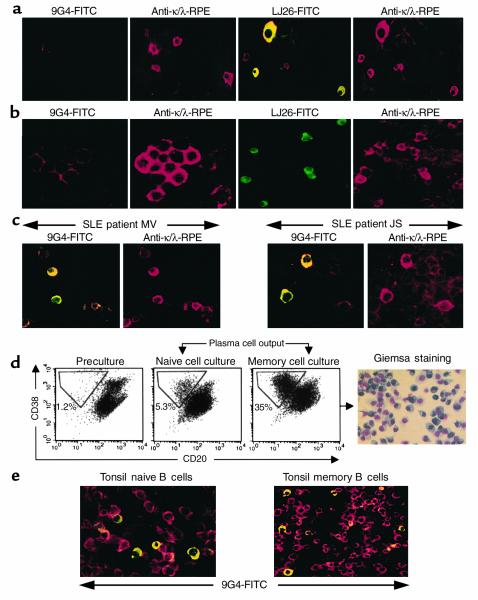
Figure 3.
Expression of VH4-34 antibodies in plasma cells from healthy donors and SLE patients. (a) Bone marrow plasma cells from healthy donors were enriched using a MACS CD138 column, and the cytoplasmic expression of VH4-34 or VH3 antibodies was detected with anti–light chain and VH-specific anti-Id antibodies 9G4, LJ26, or LC1 (data not shown). In contrast to VH3 and other VH4 antibodies, expression of VH4-34 was absent from normal plasma cells. (b) Identical results were obtained with tonsillar cells. (c) Plasma cells from the peripheral blood of active SLE patients express VH4-34 antibodies with significant frequency (two representative examples are shown). Further analysis revealed that more than 95% of VH4-34 antibodies were of the IgG isotype (data not shown). (d) Differentiation of VH4-34 B cells into plasma cells in vitro. Naive and memory tonsil B cells were sorted and independently cultured in the presence of CD70, IL-2, and IL-10 as described. The frequency of plasma cells was determined by flow cytometry before fractionation (left panel) and after culture (middle panels), and morphological confirmation was obtained by Giemsa staining (right panel). Significant numbers of plasma cells with a CD38Hi/CD20Lo phenotype were obtained with naive and memory cell cultures. (e) Plasma cells obtained in culture were analyzed for intracellular expression of VH4-34 antibodies using FITC-conjugated 9G4 and anti-κ/λ-RPE. VH4-34+ plasma cells were detected at a frequency consistent with the relative abundance of VH4-34 cells in the initial samples and therefore were significantly higher in the naive cell cultures than in the memory cell cultures.