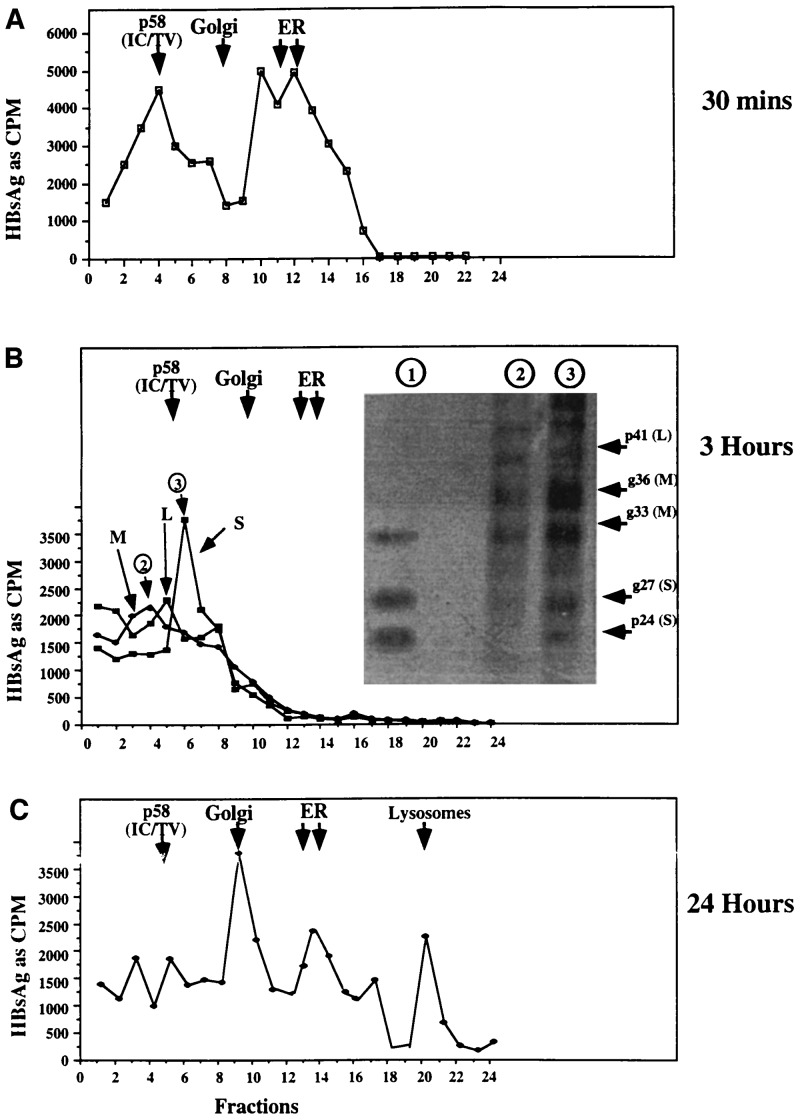
Figure 3.
Intracellular distribution of HBsAg L, M, or S in glucosidase-inhibited cells. Cytoplasmic lysates from 2.15 cells, maintained for 3 h in the absence or presence of glucosidase inhibitor, were labeled with [35S]methionine for 20 min, as in Fig. 1. At various times after labeling, immediately after the label (A; 30 min) or at 3 h (B) and 24 h (C), cytoplasmic lysates were prepared and resolved through Percoll gradients, as in Fig. 2. The positions of the peaks of the markers associated with the Golgi and ER (WGA and G6PD) are shown as arrows. Each fraction was probed for the presence of HBsAg by the antigen capture method using mAb. mAbs were used as follows: H166 (A); MA/18 (L), E (for M and L) and C20-02 for S (B). The amount of antigen bound to plates containing mAb was determined by cpm. (B Inset) Fractions 4 and 6 (indicated by circled 2 and 3) from the Percoll gradient shown in B were disrupted by sonication, and polypeptides were immunoprecipitated with an antibody that recognizes an epitope common to S, M, and L, and resolved by SDS/PAGE. An immunoprecipitate of HBV subviral particles prepared from the culture medium of control 2.15 cells 24 h after radiolabeling with [35S]methionine are also shown (lane 1). The autoradiographic image is presented. The relative positions of mono- and diglycosylated M (gp33 and gp36) as well as unglycosylated and monoglycosylated S (p24 and gp27) are also shown.