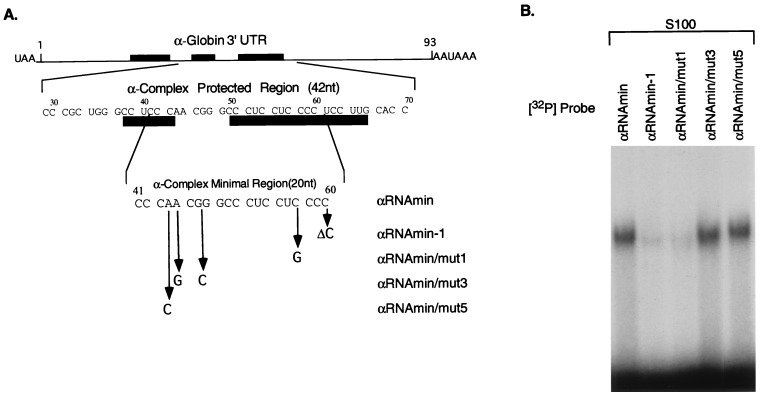
Figure 2.
A 20-nt segment of α-globin 3′UTR is sufficient for α-complex assembly. (A) The diagram represents the α-globin mRNA 3′UTR. The first sequence below the diagram is that of the 42-nt region of the 3′UTR protected from RNase digestion by the α-complex (protected region). The filled rectangles indicate positions of the pyrimidine-rich sequence elements of the α-globin stability complex (6). Numbers above the sequence indicate nucleotide position starting from the first nucleotide after the translational stop signal UAA. The second sequence represents the minimal binding site of the α-complex (αRNAmin) as determined by terminal deletion mapping (data not shown). Mutations in αRNAmin that were tested for their effects on α-complex assembly are indicated below this sequence. (B) RNP complex assembly on the αRNAmin and on four derivative mutant sequences. Gel mobility-shift assays were performed on equal amounts (documented by analysis by denaturing gel electrophoresis; data not shown) of each of the indicated mutant RNA segments (detailed in A) using S100 extract from K562 cells.