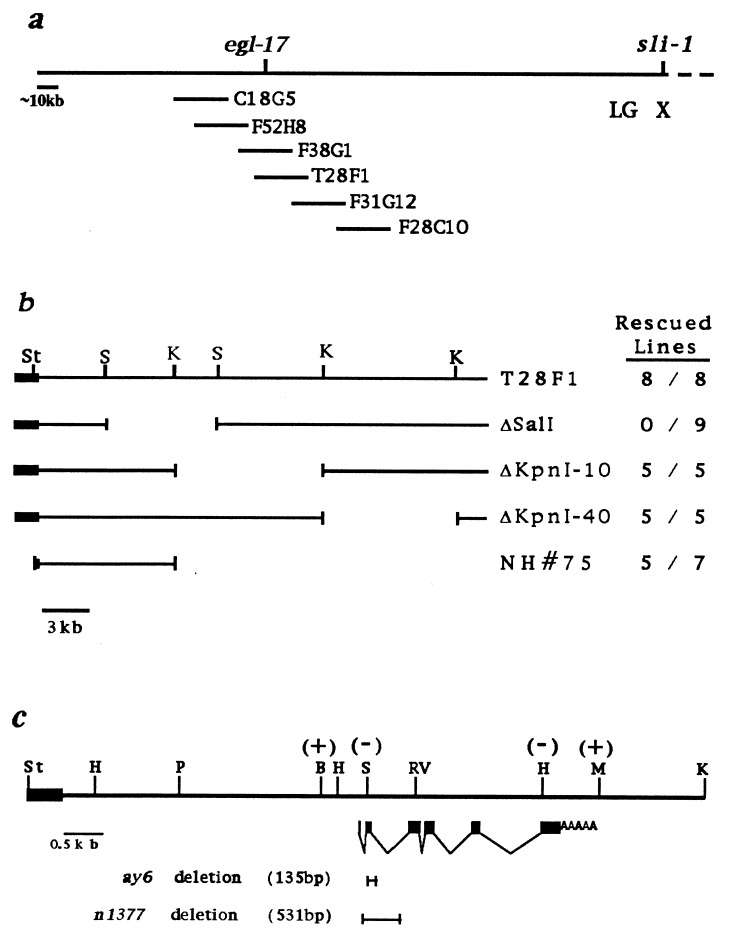
Figure 1.
Molecular mapping of egl-17. (a) Cosmids from the left end of the X chromosome contig are shown. The Egl defect of egl-17 mutants is rescued by cosmids F38G1 and T28F1, but not by the adjacent cosmids shown. (b) Restriction map of cosmid T28F1 and subclones used to determine the smallest region containing egl-17-rescuing activity. Rescued lines, fraction of stable lines rescued out of the total number of lines scored. The solid bar represents cosmid vector sequences. (c) Genomic structure of the egl-17 transcript within the 9.1-kb rescuing fragment. The 7.0-kb PstI–KpnI fragment also shows egl-17 rescuing activity albeit at somewhat reduced efficiency. Vector sequences are depicted as in b. Solid boxes represent exons; poly(A) tail is indicated. The effects of 4-bp insertion mutations are indicated within parenthesis: +, rescuing activity retained; −, rescuing activity abolished. Extent of allele-specific deletions are depicted by bracket bars. B, BglII; RV, EcoRV; H, HindIII; K, KpnI; M, MluI; P, PstI; S, SalI; St, StuI.