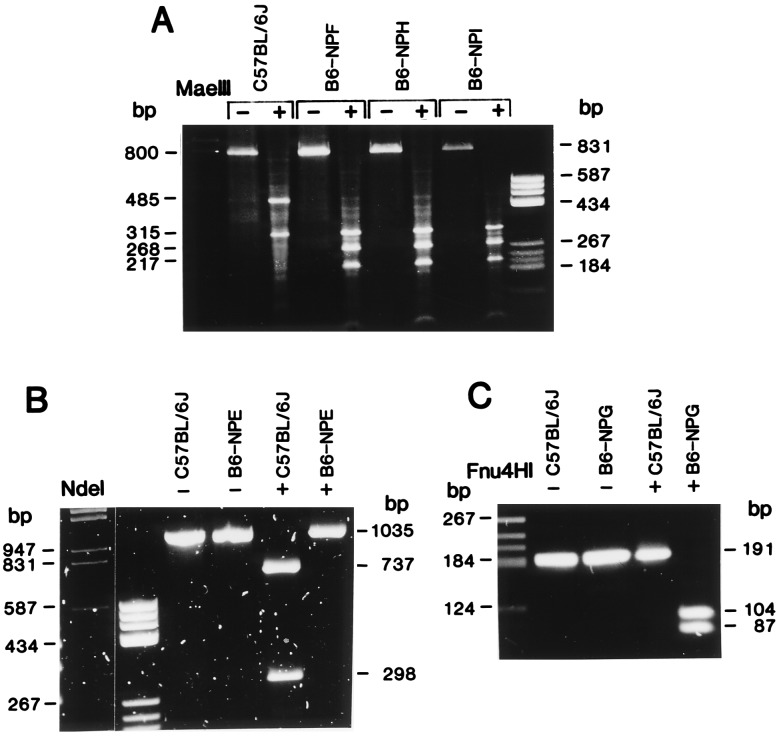
Figure 1.
PCR–restriction fragment length polymorphism analyses of nucleotide substitutions found in PNP-deficient mice. (A) Genomic DNA isolated from brain was amplified with 5′Npc2 and 3′Npnc2 primers to produce a fragment of approximately 800 bp containing 391 bp of exon. C57BL/6J, expressing the Npb allele, has a single MaeIII restriction site within an intron, resulting in 485- and 315-bp fragments. The G → A substitution at nucleotide 682 in the B6-NPF, B6-NPI, and B6-NPH variant strains produces an additional restriction site at base pair 678, resulting in digestion of the 485-bp fragment to 268- and 217-bp fragments. (B) C57BL/6J and B6-NPE cDNAs were amplified with 5′Npnc1 and 3′Npnc2 primers, producing a 1035-bp product. C57BL/6J contains a single NdeI site at nucleotide 257, resulting in 737- and 298-bp fragments. B6-NPE has lost this site as a result of the T → A substitution at nucleotide 260. (C) C57BL/6J and B6-NPG cDNAs were amplified with 5′Npnc1 and 3′Npc150 primers, producing a 191-bp fragment. B6-NPG contains a single Fnu4HI site at base pair 46 due to the T → C substitution at nucleotide 46, resulting in 104- and 87-bp fragments. This site is absent in C57BL/6J, resulting in an undigested 191-bp band.