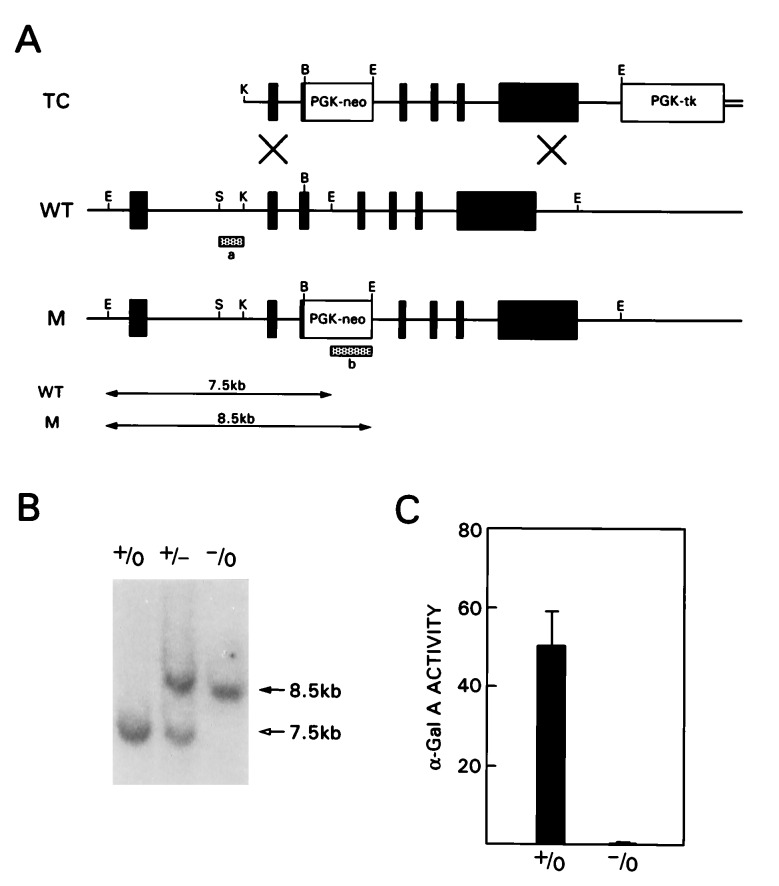
Figure 1.
Targeted disruption of the α-Gal A gene in mouse ES cells and generation of α-Gal A(−/0) mice. (A) Schematic representation of the targeting construct (TC) and the wild-type (WT) and mutated (M) alleles of α-Gal A gene. The hatched bars indicate 5′ flanking probe (a) and neomycin resistance gene (neo) probe (b) used to identify targeted clones. Restriction enzyme sites are as follows: K, KpnI; B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; S, SacI. (B) A representative Southern blot analysis of tail DNA from α-Gal A(+/0), α-Gal A(+/−), and α-Gal A(−/0) mice hybridized with probe a. (C) α-Gal A activity in liver homogenates from α-Gal A(+/0) (n = 6) and α-Gal A(−/0) (n = 5) mice. Activities are expressed as nmol/h per mg protein. Bar = SD.