Fig. 3.
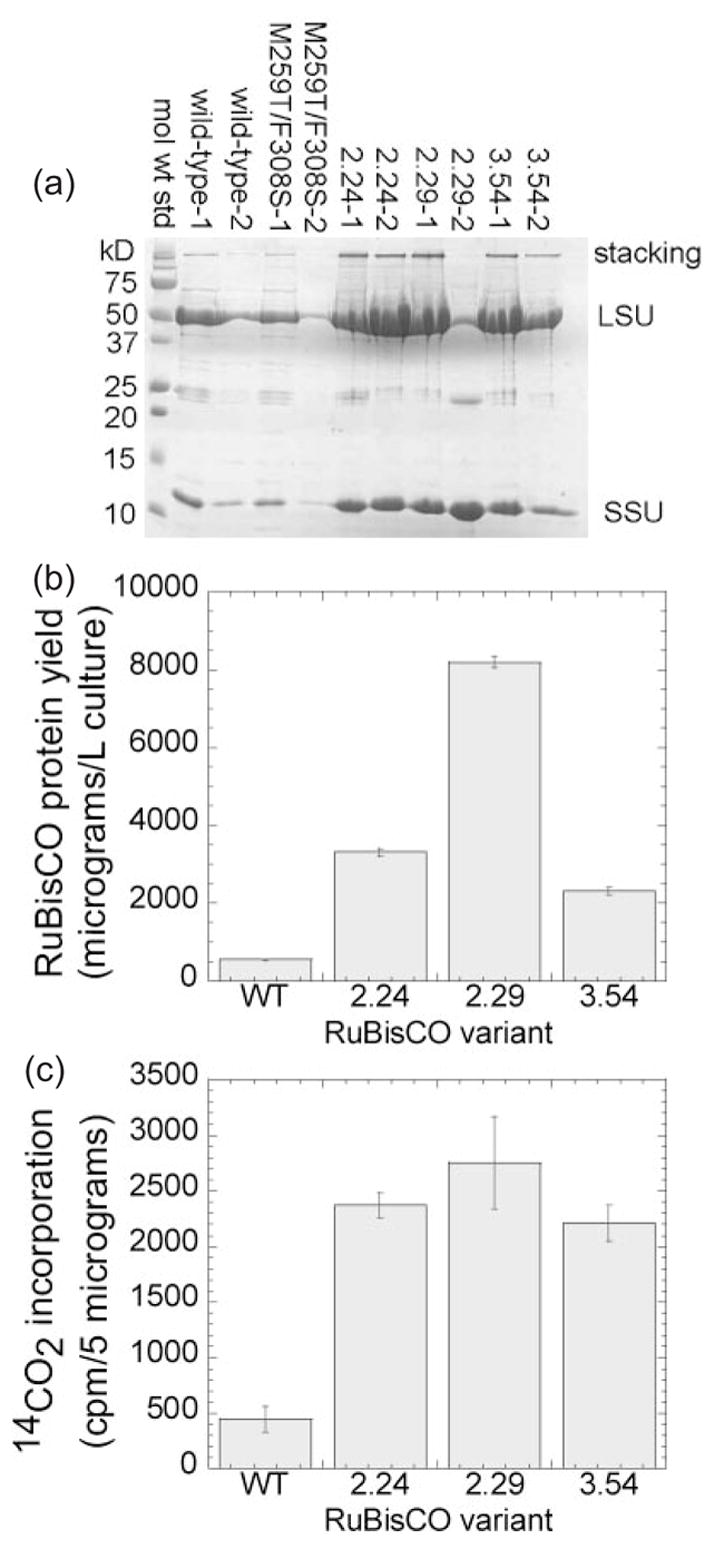
Mutations in rbcL improve purification yields of RuBisCO protein and specific activity in vitro (a) Hexa-histidine-tagged versions of the wild-type and three evolved Synechococcus rbcL variants were co-expressed in E.coli with the wild-type rbcS. The cells were lysed, and the RuBisCO was purified by IMAC and analyzed by SDS–PAGE as described in the text. (b) The purification yields of the C-terminal his-tagged RuBisCO clones (a) were determined by the Bradford protein assay, using BSA as a standard. (c) Equal quantities (5 μg) of each purified RuBisCO were reacted with ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate and NaH14CO3; the reactions were quenched with HCl; the unincorporated 14CO2 was evaporated and the rate of 3-phosphoglycerate product formation was measured in a scintillation counter.
