Abstract
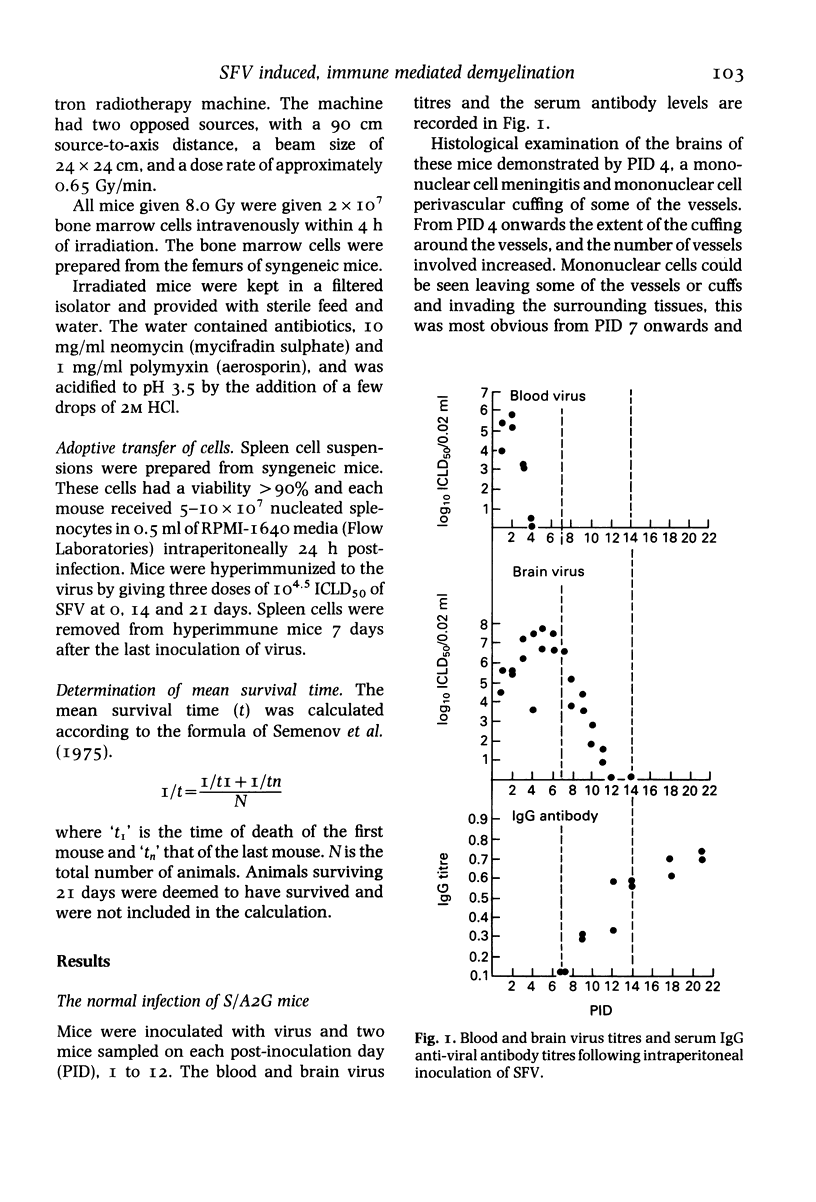
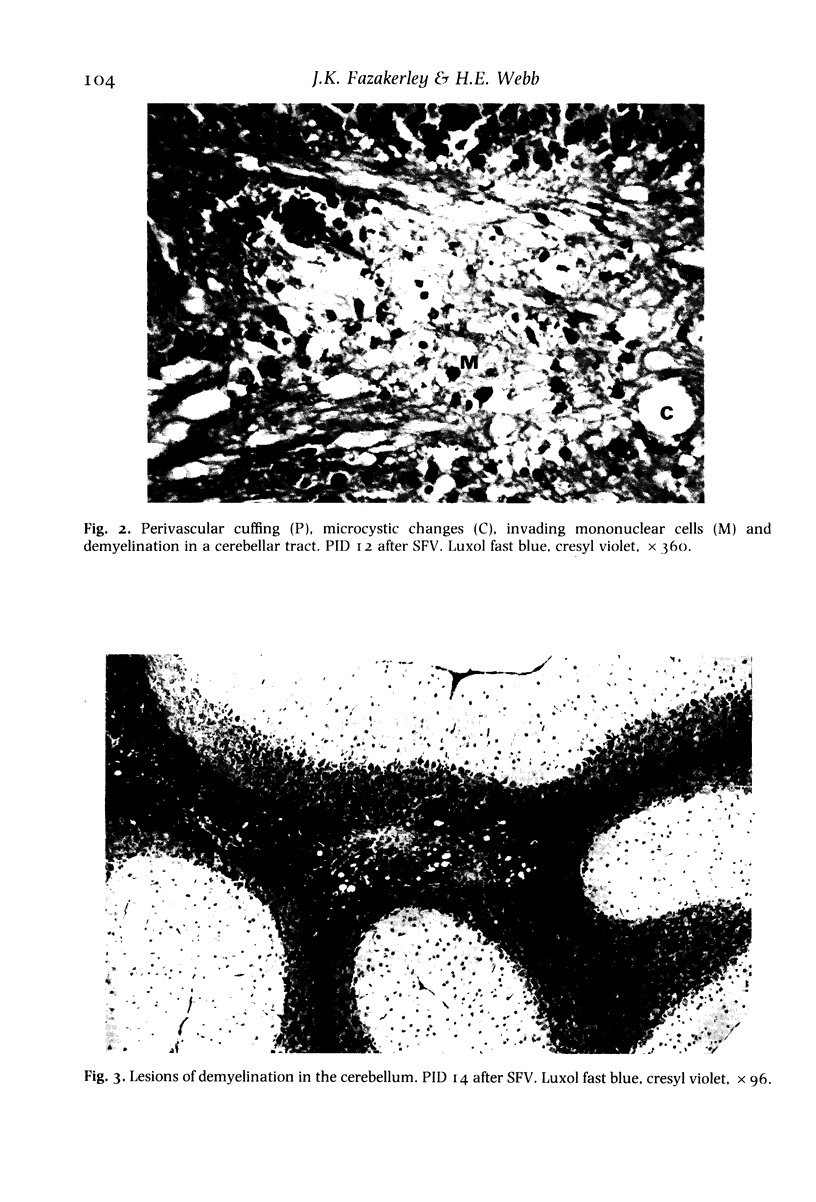
Intraperitoneal infection with the avirulent A7(74) strain of the alphavirus Semliki Forest virus (SFV) induces an immune mediated demyelinating encephalomyelitis. The blood and brain virus titres, the serum antibody titres and the histopathological changes in the brains of normal mice and mice immunosuppressed with 5.0 or 8.0 Gy total body irradiation (TBX) were determined. SFV infection of immunosuppressed mice resulted in persistently high blood and brain virus titres, neuronal pycnosis, paralysis and death. No demyelination or central nervous system (CNS) inflammatory response occurred in these immunosuppressed mice despite high and persistent brain virus titres. The CNS inflammatory response and associated demyelination could be restored to infected immunosuppressed mice by adoptive transfer of spleen cells, and these changes were brought forward if the donor spleen cells were from mice previously sensitized to SFV. The results indicate that the immune response following SFV A7(74) infection is both protective and pathogenic, and that the demyelination is immune mediated and does not result from direct viral destruction of oligodendrocytes, or any other direct effect of the virus.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins G. J., Sheahan B. J., Dimmock N. J. Semliki Forest virus infection of mice: a model for genetic and molecular analysis of viral pathogenicity. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):395–408. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins G. J. The avirulent A7 Strain of Semliki Forest virus has reduced cytopathogenicity for neuroblastoma cells compared to the virulent L10 strain. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jun;64(Pt 6):1401–1404. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-6-1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett P. N., Sheahan B. J., Atkins G. J. Isolation and preliminary characterization of Semliki Forest virus mutants with altered virulence. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jul;49(1):141–147. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruton C. J., Kennedy S. I. Defective-interfering particles of Semliki Forest Virus: structural differences between standard virus and defective-interfering particles. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):383–395. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chew-Lim M. Mouse encephalitis induced by avirulent Semliki forest virus. Vet Pathol. 1975;12(5-6):387–393. doi: 10.1177/0300985875012005-00605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
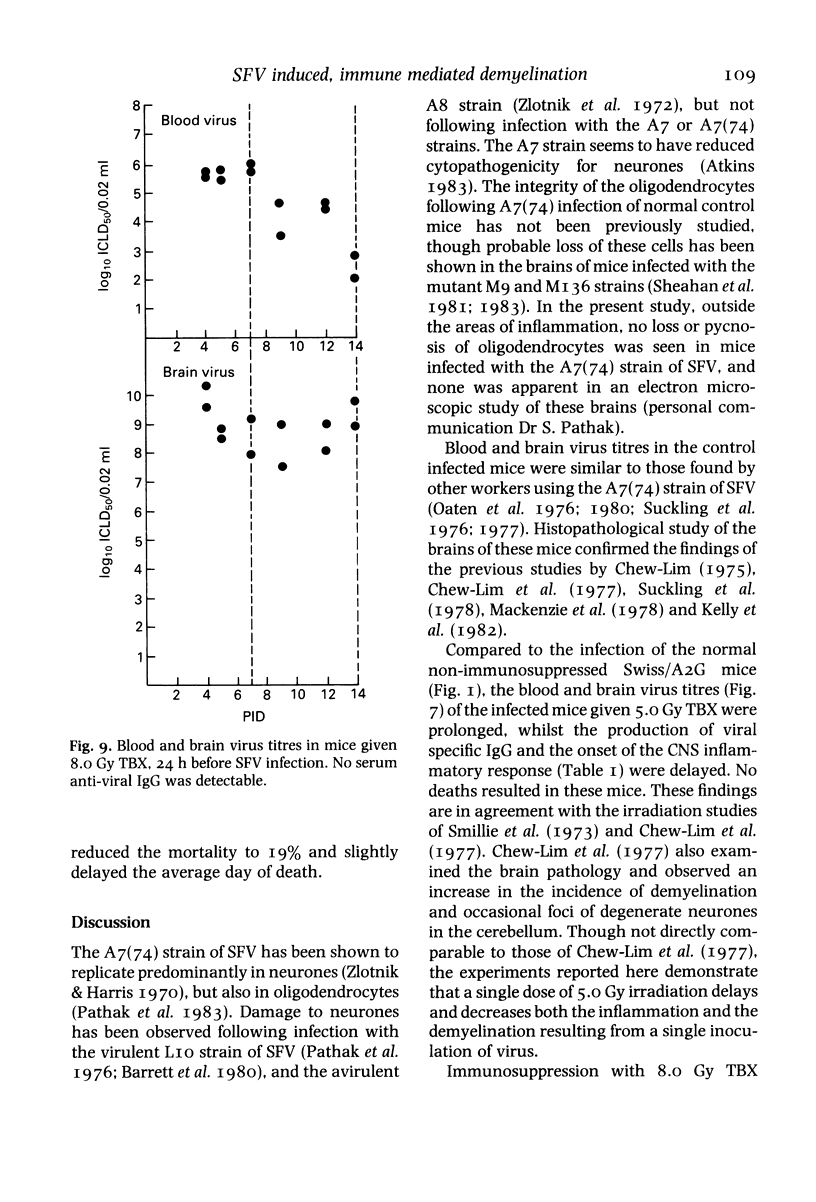
- Chew-Lim M., Webb H. E., Jagelman S. The effect of irradiation on demyelination induced by avirulent Semliki Forest virus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1977 Oct;58(5):459–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doria G., Agarossi G., Adorini L. Selective effects of ionizing radiations on immunoregulatory cells. Immunol Rev. 1982;65:23–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
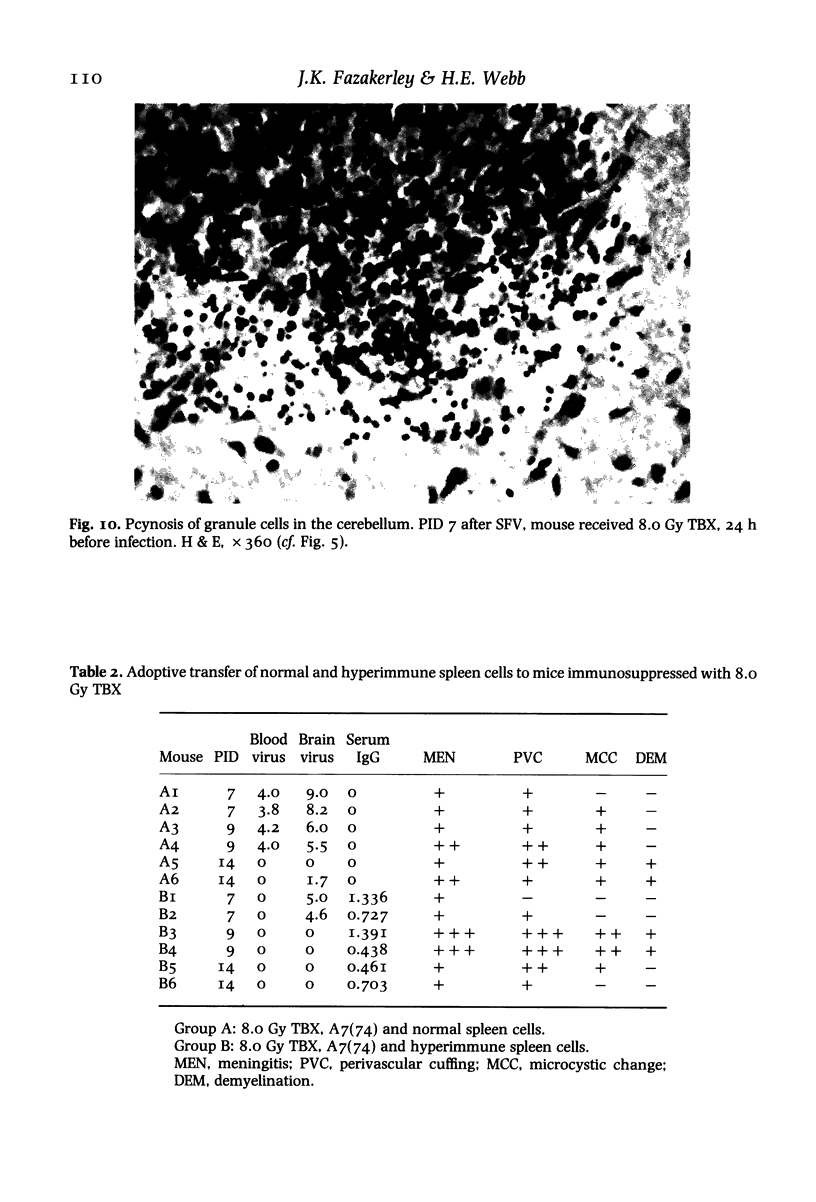
- Fazakerley J. K., Amor S., Webb H. E. Reconstitution of Semliki forest virus infected mice, induces immune mediated pathological changes in the CNS. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Apr;52(1):115–120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming P. Age-dependent and strain-related differences of virulence of Semliki Forest virus in mice. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):93–105. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illavia S. J., Webb H. E., Pathak S. Demyelination induced in mice by avirulent Semliki Forest virus. I. Virology and effects on optic nerve. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1982 Jan-Feb;8(1):35–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1982.tb00255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagelman S., Suckling A. J., Webb H. E., Bowen F. T. The pathogenesis of avirulent Semliki Forest virus infections in athymic nude mice. J Gen Virol. 1978 Dec;41(3):599–607. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-3-599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie A., Suckling A. J., Jagelman S., Wilson A. M. Histopathological and enzyme histochemical changes in experimental Semliki Forest virus infection in mice and their relevance to scrapie. J Comp Pathol. 1978 Jul;88(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(78)90038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Glasgow L. A. Factors modifying host resistance to viral infection. 3. Effect of whole body x-irradiation on experimental encephalomyocarditis virus infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):1035–1052. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaten S. W., Jagelman S., Webb H. E. Further studies of macrophages in relationship to avirulent Semliki Forest virus infections. Br J Exp Pathol. 1980 Apr;61(2):150–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaten S. W., Webb H. E., Bowen E. T. Enhanced resistance of mice to infection with Langat (TP21) virus following pre-treatment with Sindbis or Semliki forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):381–388. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. M., Griffin D. E., Johnson R. T. Studies of immune responses during recovery from Sindbis virus encephalitis in selectively reconstituted, thymectomized, lethally irradiated mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):306–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.306-309.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons L. M., Webb H. E. Blood brain barrier disturbance and immunoglobulin G levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of the mouse following peripheral infection with the demyelinating strain of Semliki Forest virus. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Dec;57(2-3):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons L. M., Webb H. E. Virus titres and persistently raised white cell counts in cerebrospinal fluid in mice after peripheral infection with demyelinating Semliki Forest virus. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1982 Sep-Oct;8(5):395–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1982.tb00307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak S., Webb H. E., Oaten S. W., Bateman S. An electron-microscopic study of the development of virulent and avirulent strains of Semliki forest virus in mouse brain. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Jul;28(3):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusztai R., Gould E. A., Smith H. Infection patterns in mice of an avirulent and virulent strain of Semliki Forest virus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Dec;52(6):669–677. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheahan B. J., Barrett P. N., Atkins G. J. Demyelination in mice resulting from infection with a mutant of Semliki Forest virus. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;53(2):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00689993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheahan B. J., Gates M. C., Caffrey J. F., Atkins G. J. Oligodendrocyte infection and demyelination produced in mice by the M9 mutant of Semliki Forest virus. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;60(3-4):257–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00691874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smillie J., Pusztai R., Smith H. Studies of the influence of host deference mechanisms on infection of mice with an avirulent or virulent strain of Semliki Forest virus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1973 Jun;54(3):260–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckling A. J., Pathak S., Jagelman S., Webb H. E. Virus-associated demyelination. A model using avirulent Semliki Forest virus infection of mice. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Nov;39(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremain K. E., Ikeda H. Physiological deficits in the visual system of mice infected with Semliki Forest virus and their correlation with those seen in patients with demyelinating disease. Brain. 1983 Dec;106(Pt 4):879–895. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.4.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb H. E., Wight D. G., Wiernik G., Platt G. S., Smith C. E. Langat virus encephalitis in mice. II. The effect of irradiation. J Hyg (Lond) 1968 Sep;66(3):355–364. doi: 10.1017/s002217240004122x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik I., Harris W. J. The changes in cell organelles of neurons in the brains of adult mice and hamsters during Semliki Forest virus and louping ill encephalitis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Feb;51(1):37–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]