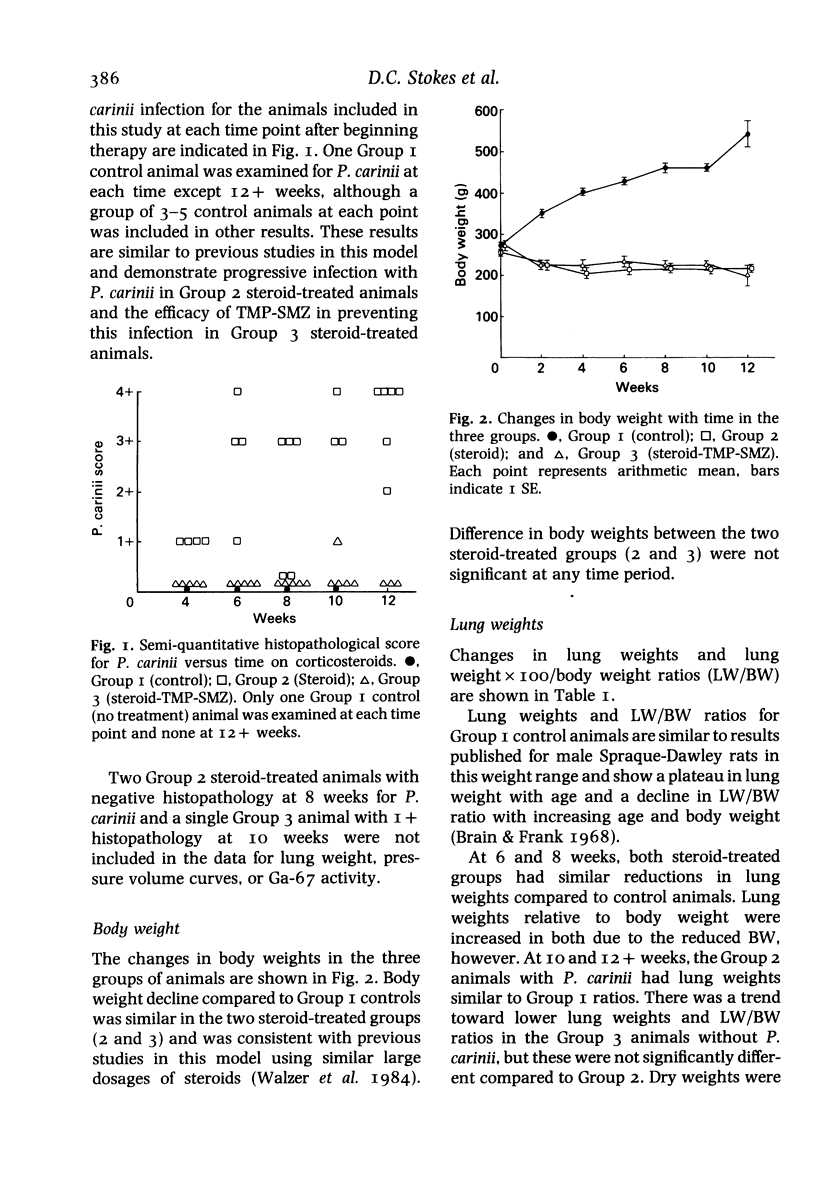
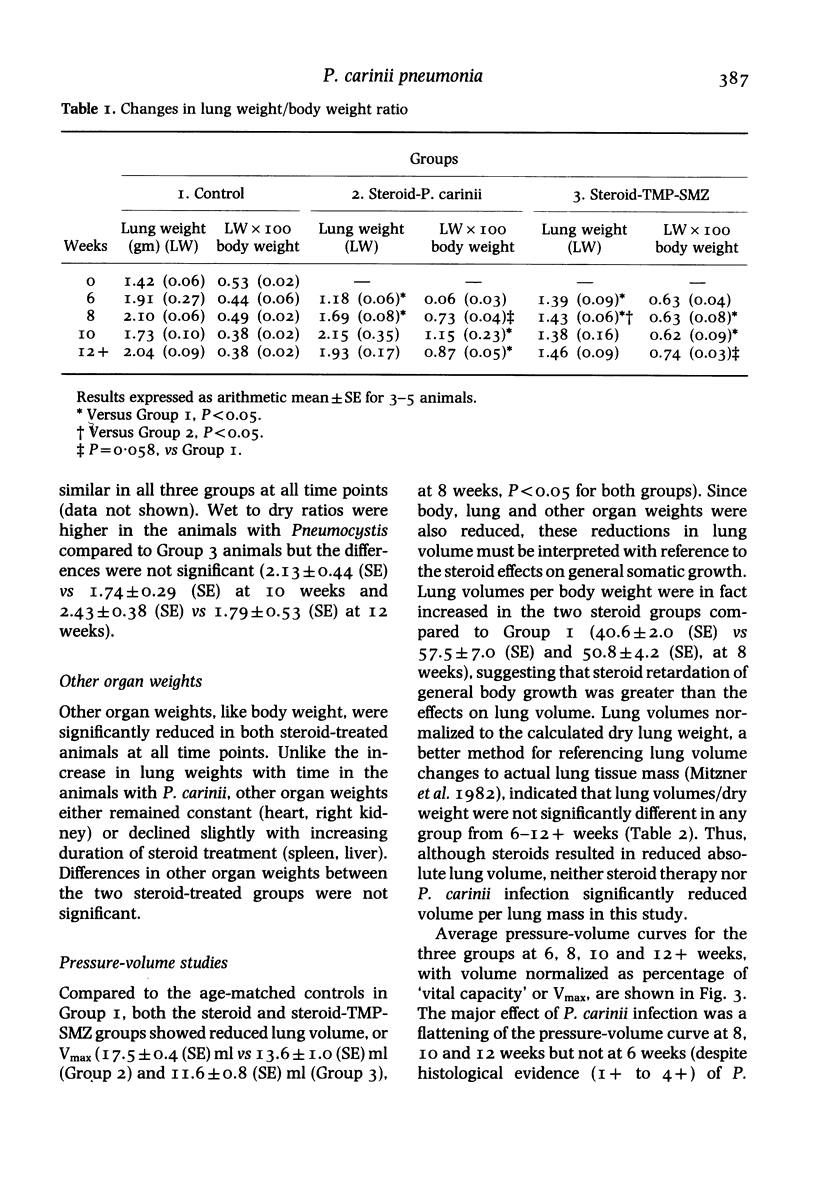
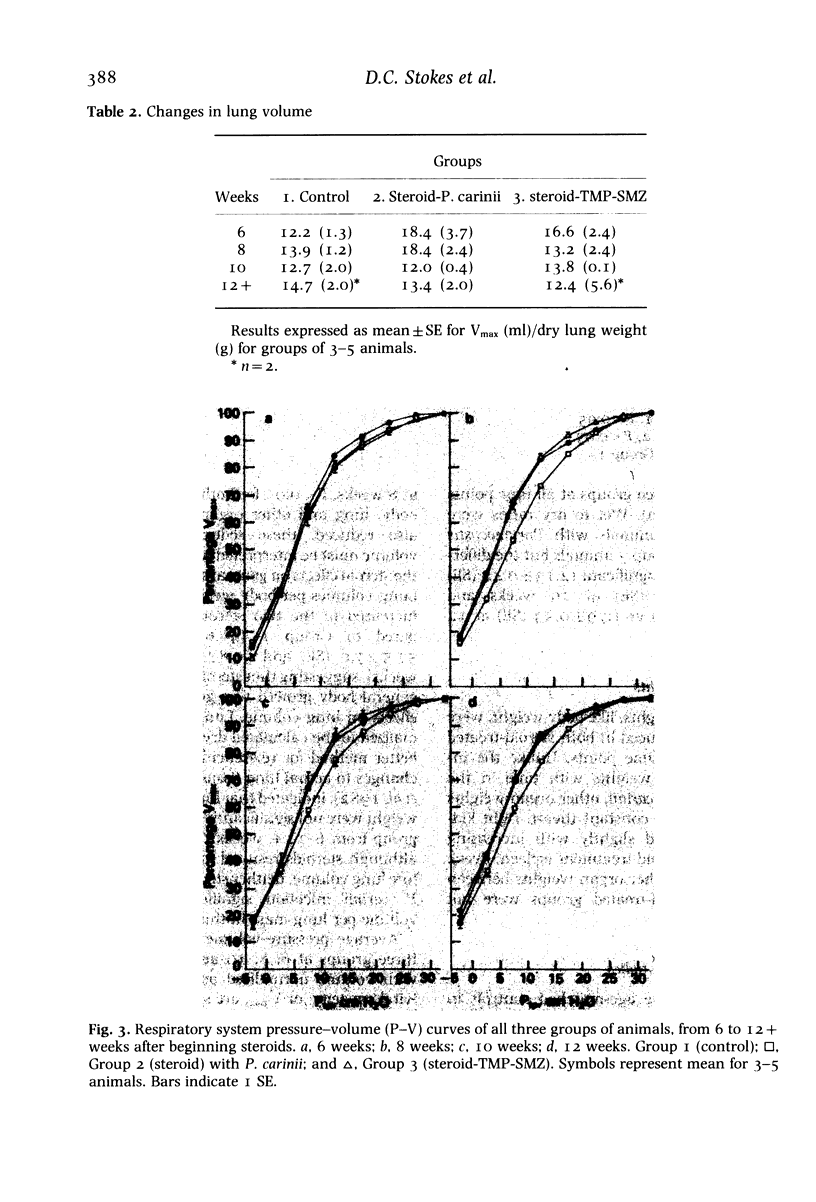
Abstract
Respiratory system pressure-volume (P-V) studies, 67Ga-citrate scans, and chest radiographs were made in the corticosteroid-treated rat model of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. The steroid treatment used to provoke Pneumocystis infection in this model resulted in a reduction in body weight, lung weight and lung volumes compared to age-matched controls but no change in the normalized pressure-volume curve. P. carinii infection was associated with increased lung wet weight and flattening of the respiratory system P-V curve when compared to either age matched controls or steroid-treated animals on trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis for P. carinii. Radiographs were interpreted as positive in only three of 11 animals with P. carinii, whereas 10 of 12 animals showed positive gallium-67 lung scans. We conclude that both gallium uptake and altered lung mechanics occur in the rat with Pneumocystis carinii and may reflect increased alveolar permeability and surfactant abnormalities noted in other studies.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brain J. D., Frank N. R. The relation of age to the numbers of lung free cells, lung weight, and body weight in rats. J Gerontol. 1968 Jan;23(1):58–62. doi: 10.1093/geronj/23.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun-Pascaud M., Pocidalo J. J., Kernbaum S. Respiratory and pulmonary alterations in experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in rats. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1985 Jan-Feb;21(1):37–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B. A., Good R. A. Pneumocystis carinii infection. Medicine (Baltimore) 1973 Jan;52(1):23–51. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197301000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Hattner R. S., Luce J. M., Dodek P. M., Golden J. A., Murray J. F. Correlation between gallium lung scans and fiberoptic bronchoscopy in patients with suspected Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Dec;130(6):1166–1169. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.6.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Pneumocystis pneumonia: a plague of the immunosuppressed. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1978 Dec;143(6):184–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernbaum S., Masliah J., Alcindor L. G., Bouton C., Christol D. Phospholipase activities of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in rat Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Br J Exp Pathol. 1983 Feb;64(1):75–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Y. L., Hildebrandt J. Respiratory mechanics in the anesthetized rat. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Aug;45(2):255–260. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson S. M., Warren R. D., Richman S. D., Johnston G. S., Chabner B. A. Abnormal pulmonary gallium accumulation in P. carinii pneumonia. Radiology. 1976 May;119(2):395–398. doi: 10.1148/119.2.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thadepalli H., Rambhatla K., Mishkin F. S., Khurana M. M., Niden A. H. Correlation of microbiologic findings and 67gallium scans in patients with pulmonary infections. Chest. 1977 Oct;72(4):442–448. doi: 10.1378/chest.72.4.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turbiner E. H., Yeh S. D., Rosen P. P., Bains M. S., Benua R. S. Abnormal gallium scintigraphy in Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia with a normal chest radiograph. Radiology. 1978 May;127(2):437–438. doi: 10.1148/127.2.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., LaBine M., Redington T. J., Cushion M. T. Lymphocyte changes during chronic administration of and withdrawal from corticosteroids: relation to Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2502–2508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Powell R. D., Jr, Yoneda K., Rutledge M. E., Milder J. E. Growth characteristics and pathogenesis of experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):928–937. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.928-937.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner R., Hoffer P. B., Thakur M. L. Lactoferrin: its role as a Ga-67-binding protein in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Nucl Med. 1981 Jan;22(1):32–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda K., Walzer P. D. Mechanism of pulmonary alveolar injury in experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the rat. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Aug;62(4):339–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]