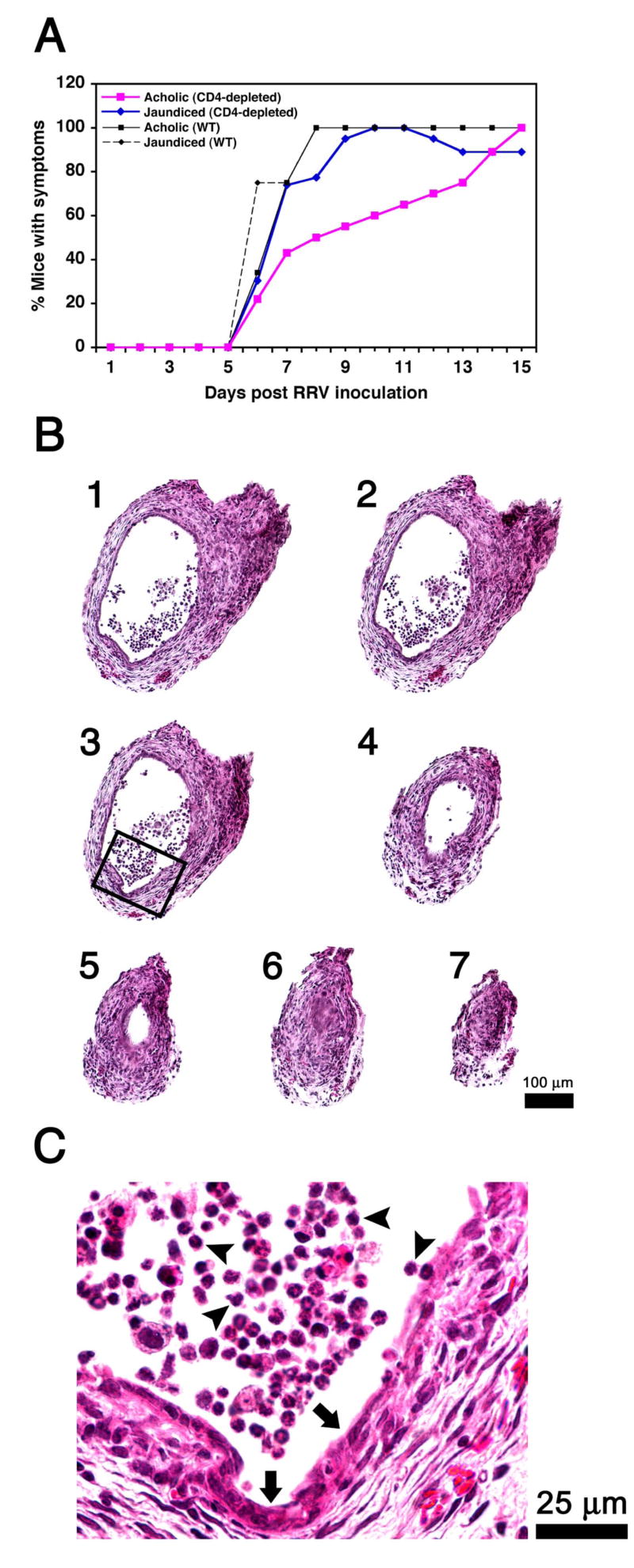
Figure 2. Loss of CD4+ cells does not modify the course of bile duct obstruction.
The onset of jaundice and acholic stools following RRV challenge in Balb/c mice was mildly delayed but the final appearance of symptoms in all mice was not altered by the antibody-mediated depletion of CD4+ cells (A). In B, successive cross-sectional views of bile ducts of CD4-depleted mice show infiltration of duct lumen by inflammatory cells (sections 1-4) and luminal obstruction (sections 5-7). The rectangle in section #3 is magnified in C, depicting epithelial injury and loss (arrows) and adjacent inflammatory cells (arrowheads). Hematoxylin/eosin stain; N=22 for WT mice infected with RRV; N=24 for CD4-depleted mice infected with RRV; sections are numbered from 1 to 7 to denote direction from the liver to the duodenum; WT = wild-type mice not injected with antibodies.