Full text
PDF







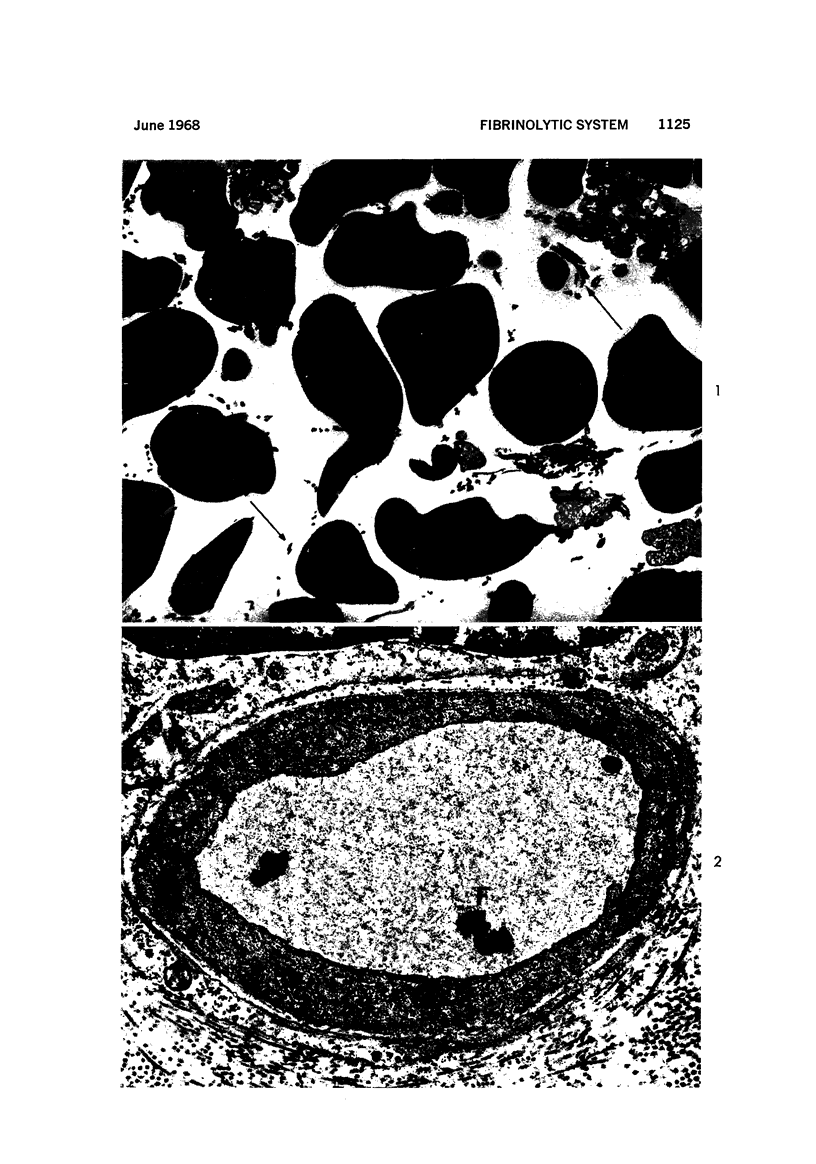

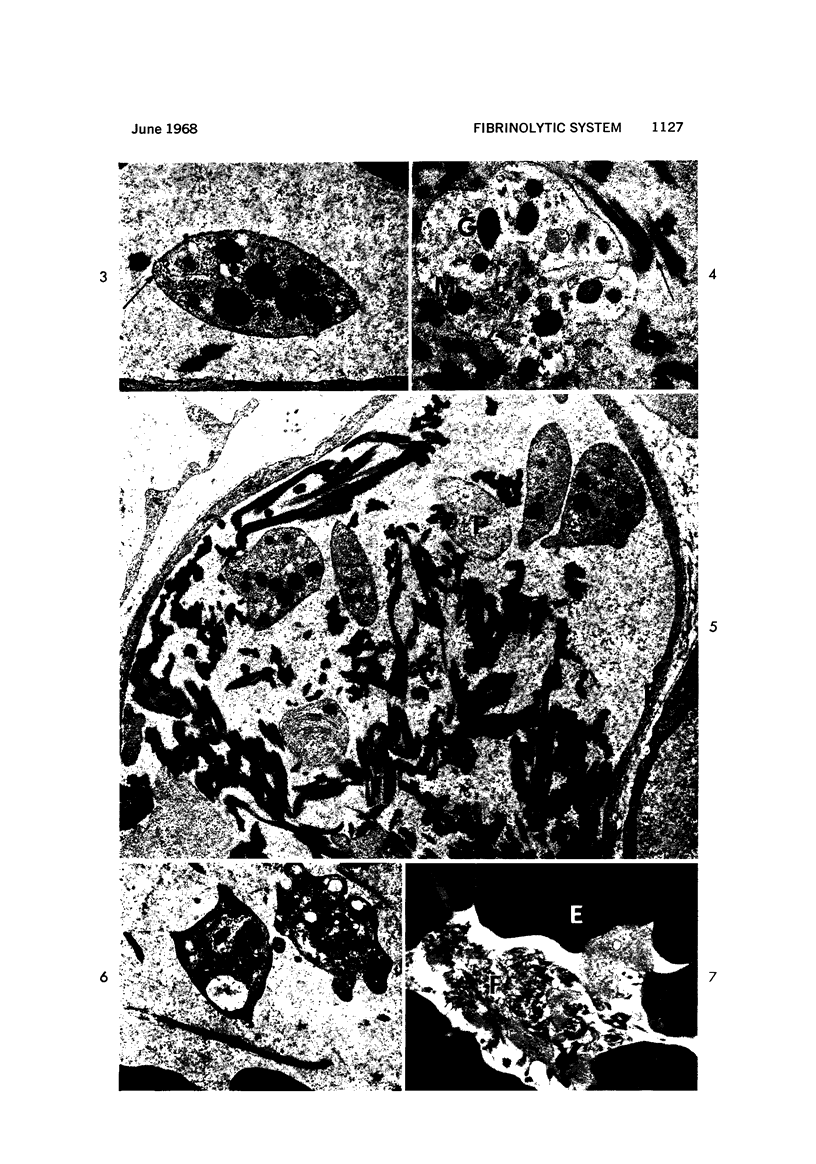
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashford T. P., Frieiman D. G. The role of the endothelium in the initial phases of thrombosis. An electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1967 Feb;50(2):257–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrup T. Tissue activators of plasminogen. Fed Proc. 1966 Jan-Feb;25(1):42–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOVIG T. The ultrastructure of rabbit blood platelet aggregates. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1962 Dec 20;8:455–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOWALSKI E., KOPEC M., WEGRZYNOWICZ Z. INFLUENCE OF FIBRINOGEN DEGRADATION PRODUCTS (FDP) ON PLATELET AGGREGATION, ADHESIVENESS AND VISCOUS METAMORPHOSIS. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Jan 1;10:406–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwaan H. C. Tissue fibrinolytic activity studied by a histochemical method. Fed Proc. 1966 Jan-Feb;25(1):52–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLONIG G. A modified procedure for lead staining of thin sections. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:736–739. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD A. S. Fibrinolysis autographs. Nature. 1958 Feb 15;181(4607):495–496. doi: 10.1038/181495b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESSLER S., FREIMAN D. G., SUYEMOTO J., REIMER S. M. Serum thrombotic accelerator (STA) activity: a possible key to massive venous thromboembolism in man. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1961;74:111–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESSLER S., REIMER S. M., SHEPS M. C. Biologic assay of a thrombosis-inducing activity in human serum. J Appl Physiol. 1959 Nov;14:943–946. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.6.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESSLER S., REINER L., FREIMAN D. G., REIMER S. M., LERTZMAN M. Serum-induced thrombosis. Studies of its induction, and evolution under controlled conditions in vivo. Circulation. 1959 Nov;20:864–874. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.20.5.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESSLER S. Studies in intravascular coagulation. III. The pathogenesis of serum-induced venous thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 1955 Apr;34(4):647–651. doi: 10.1172/JCI103114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]