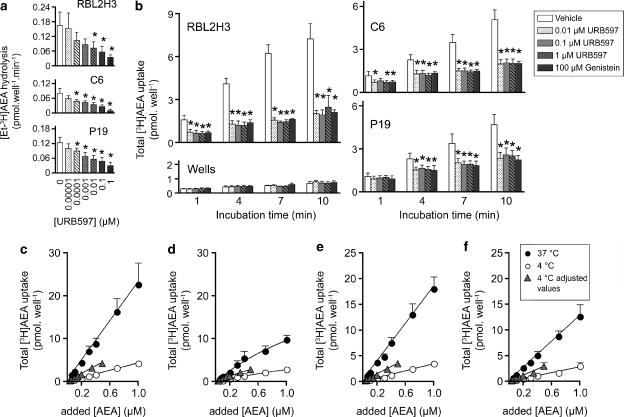
Figure 1.
The role of FAAH on the uptake of [3H]AEA. (a) Effect of URB597 upon the metabolism of 100 nM [Et-3H]AEA by RBL2H3, C6 and P19 cells. The cells were preincubated with URB597 for 10 min before addition of [Et-3H]AEA and incubation for a further 20 min . Means±s.e.m., n=4. (b) Effect of URB597 and genistein upon the uptake of 100 nM [3H]AEA by either RBL2H3, C6, P19 cells or by wells alone at different incubation times. The samples were preincubated for 15 min with either vehicle or genistein and then an additional 15 min with URB597 or vehicle before addition of AEA and incubation for the times shown. The ‘batch analysis protocol' was used (see Methods section for details). Data are means±s.e.m., n=4. *P<0.05 vs the vehicle control, Dunnett's multiple comparison following significant one-way ANOVA for repeated measures at each incubation time point. For the wells at t=4 min, one value (for 1 μM URB597) was missing, and in consequence a factorial ANOVA was used for this data set. Panels (c–f) show the total uptake of [3H]AEA (means±s.e.m., n=4) by RBL2H3 cells (c,d) and P19 cells (e, f) following an incubation time of 10 min. In (d and f), the cells were treated with 1 μM URB597. The concentrations given for AEA at 37°C are those added, whereas the concentrations for AEA at 4°C are either those added, or those added × 0.49 to compensate for the effect of assay temperature on substrate availability (‘adjusted values', see Methods for details). For both RBL2H3 and P19 cells, two-way factorial ANOVA values for the data at 37°C gave significant contributions for added AEA concentration and for URB597, whereas for the data at 4°C, the contribution by URB597 was only significant for the RBL2H3 cells.