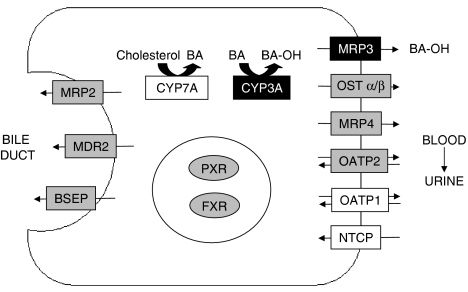
Figure 6.
Metabolism and transport of BA, and the proposed mechanism for PCN-mediated protection against CA-induced hepatotoxicity. CA feeding results in the feed-forward induction of bile acid efflux transporters and hydroxylation by CYP3A. Hepatic uptake of BA by NTCP and OATP1 and synthesis by CYP7A are downregulated. CYP3A and MRP3 are further induced by the co-administration of PCN. Thus BAs are cleared from the liver by PXR activation-dependent hydroxylation (CYP3A) and basolateral efflux (MRP3), leading to renal elimination. Genes in boxes with grey shading were induced by CA feeding, whereas those in boxes with dark shading were induced further by co-administration of PCN. Genes in boxes without shading were downregulated by CA feeding.