Figure 4.
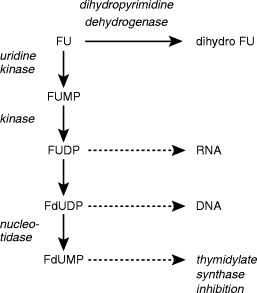
The intracellular metabolism of fluorouracil (FU). FU can either be catabolized by dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) to form dihydro FU or phosphoribosylated to form active nucleotide metabolites. The nucleotide metabolites depicted above are fluorouridine monophosphate and diphosphate, and fluoro-deoxyuridine diphosphate and monophosphate (FUMP, FUDP, FdUDP, FdUMP, respectively). Intracellular metabolism of FU and its nucleotides is analogous to uracil metabolism ]14[. FU is converted to FUMP via 5′-fluorouridine in a two step reaction catalysed by nucleoside phosphorylase and uridine kinase. It is possible that FUMP could be formed directly from the FU base via pyrimidine phosphoribosyltransferase. Phosphorylation of FUMP proceeds by nucleoside monophosphate kinase (1). Nucleoside 5′-diphosphate reductase (ribonucleotide reductase) catalyses the production of 2′-deoxribonucleotide (FdUDP) from the ribonucleotide (FUMP). Phosphate is removed from nucleotides by 5′-nucleotidases (2).
