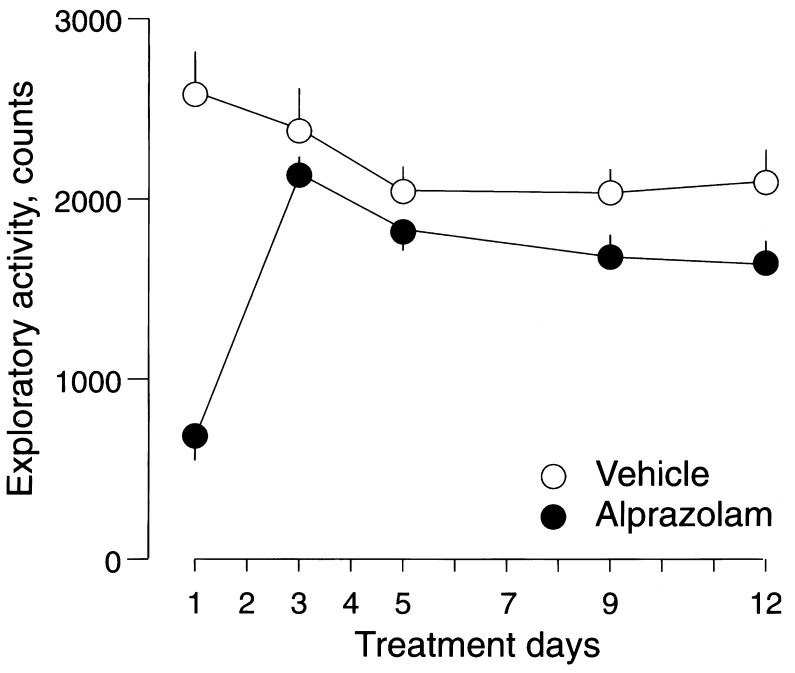
Figure 1.
Time course of changes in the exploratory activity of mice during chronic treatment with alprazolam. Circles represent mean ± SEM number of counts recorded in mice treated with vehicle (○) or alprazolam at 6 mg/kg twice daily (•). Exploratory activity was monitored for 10 min in nonhabituated mice 2 h after s.c. administration of vehicle or alprazolam. Two-way ANOVA with factors for treatment, time, and their interaction revealed a rapid development of tolerance to the sedative effect of alprazolam during chronic treatment, FT1(1,136) = 47.33, P < 0.001 vs. FT3-T12(1,136) = 1.25, P > 0.05). Experimental groups consisted of 16 mice, which were used for the monitoring of exploratory activity once only during the entire treatment with vehicle or alprazolam over 12 days. A total of 146 recordings performed in 160 mice were used for the analysis.