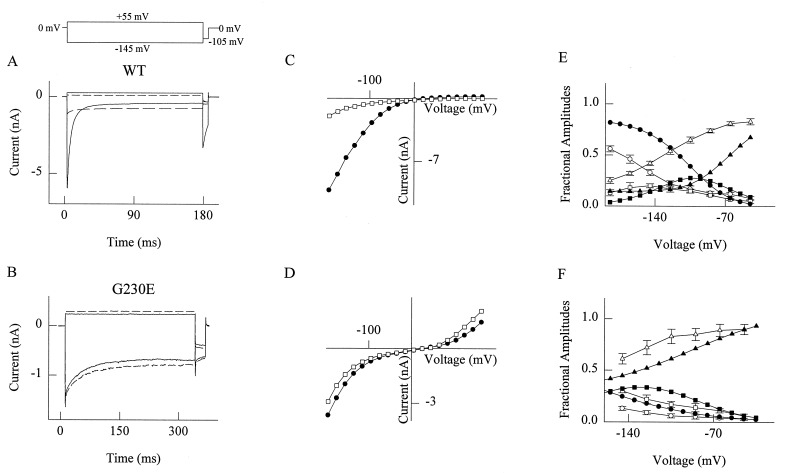
Figure 3.
Effect of extracellular iodide on WT and G230E. (A) Current responses to voltage steps from a holding potential of 0 mV to −145 mV and 55 mV recorded from a cell stably expressing WT hClC-1 channels before (solid lines) and after (dashed line) addition of 30 mM NaI to the extracellular solution. (B) Current responses to voltage steps from a holding potential of 0 mV to −145 mV and 55 mV recorded from a cell stably expressing G230E channels before (solid lines) and after (dashed line) addition of 30 mM NaI to the extracellular solution. (C and D) Voltage dependence of the instantaneous current amplitude for WT (C) and G230E (D) before (closed circles) and after (open squares) addition of 30 mM NaI to the extracellular solution. Test potentials were preceded by a 500-ms prepulse to 50 mV. (E and F) Voltage dependence of fractional current amplitudes, obtained as described in Fig. 2 for WT (E) and G230E (F). Results in the presence (open symbols) or absence (filled symbols) of extracellular 30 mM iodide. Fractional current amplitudes are: circle, A1, square, A2, and triangle, C. Data shown are mean ± SEM (n = 4).