Abstract
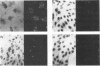
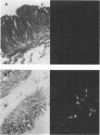
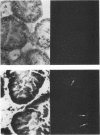
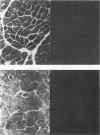
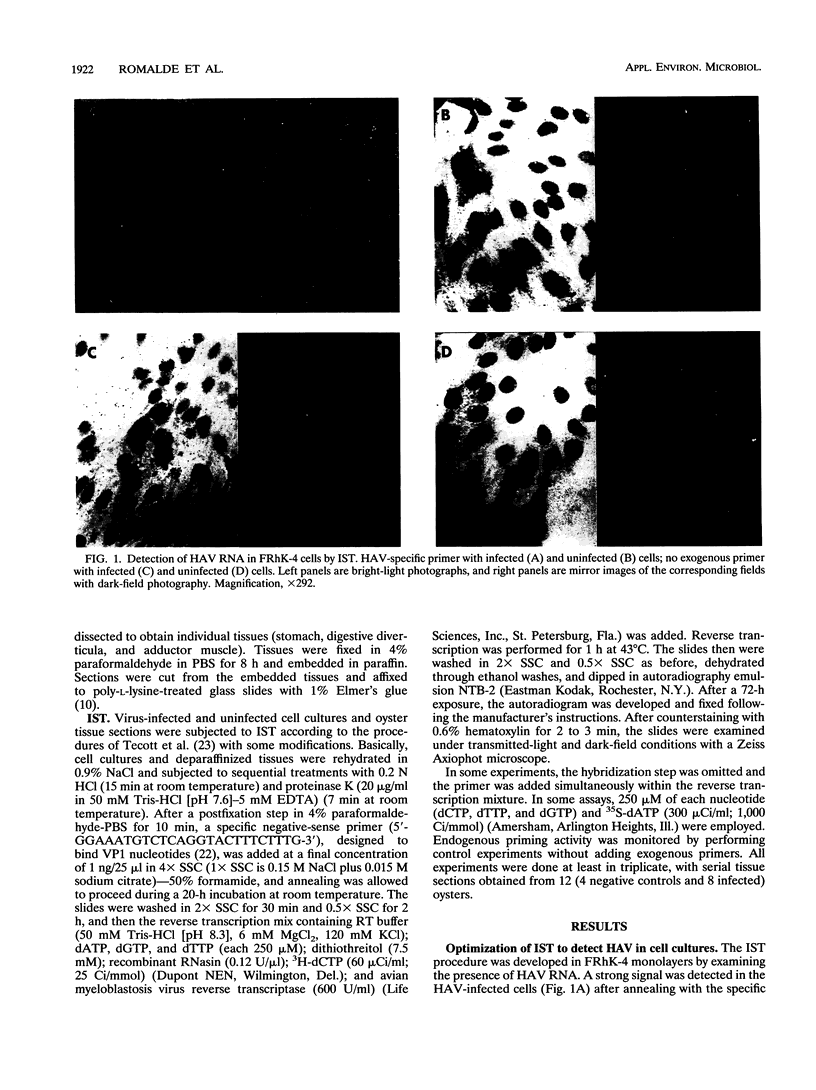
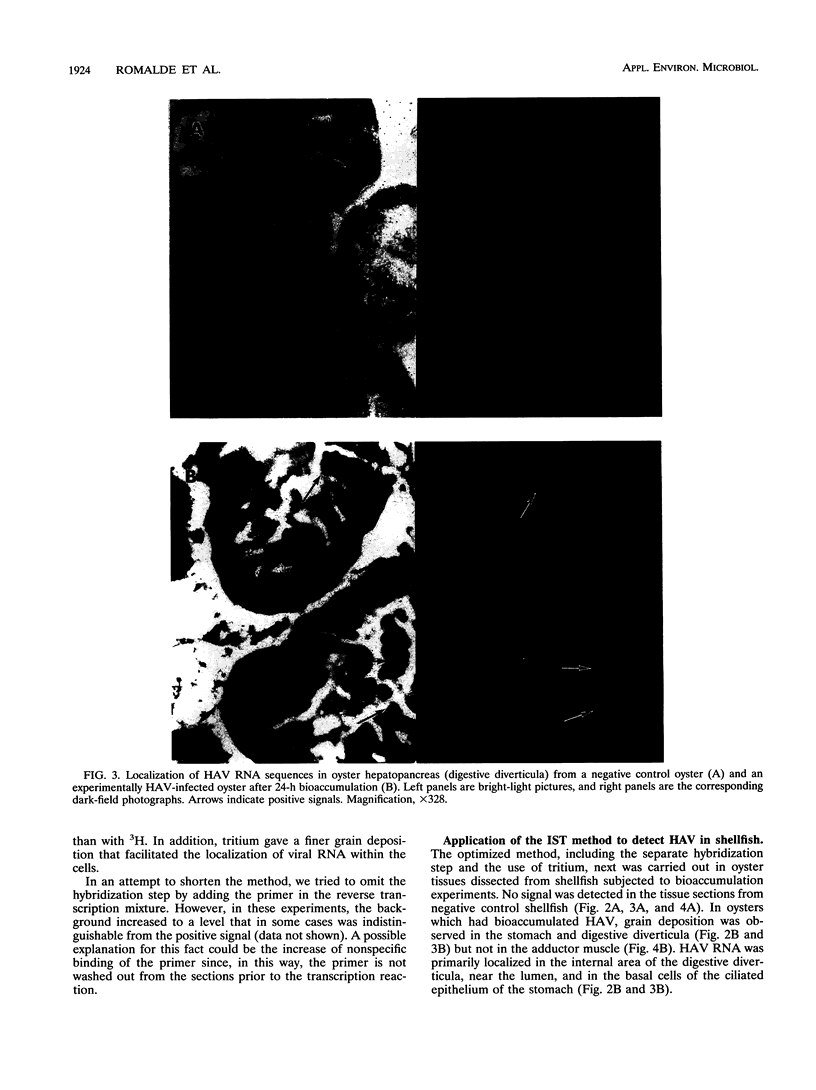
An in situ transcription method was developed to detect hepatitis A virus RNA in both cell cultures and shellfish tissues. Radiolabeled cDNA copies were synthesized in situ by reverse transcriptase-directed transcription after annealing with a specific primer to the viral RNA. Both tritium (3H) and 35S were useful in the in situ transcription reaction, but the use of 3H resulted in a lower background and finer detail in the localization of viral particles. Application of the method to different organs of oysters which had bioaccumulated hepatitis A virus allowed the first in situ localization of the virus, specifically in stomach and hepatopancreatic tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atmar R. L., Metcalf T. G., Neill F. H., Estes M. K. Detection of enteric viruses in oysters by using the polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Feb;59(2):631–635. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.2.631-635.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstens J. M., Tracy S., Chapman N. M., Gauntt C. J. Detection of enteroviruses in cell cultures by using in situ transcription. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):25–35. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.25-35.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulepis A. G., Veale M. F., MacGregor A., Kornitschuk M., Gust I. D. Detection of hepatitis A virus and antibody by solid-phase radioimmunoassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):119–124. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.119-124.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deinhardt F., Gust I. D. Viral hepatitis. Bull World Health Organ. 1982;60(5):661–691. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desenclos J. C., Klontz K. C., Wilder M. H., Nainan O. V., Margolis H. S., Gunn R. A. A multistate outbreak of hepatitis A caused by the consumption of raw oysters. Am J Public Health. 1991 Oct;81(10):1268–1272. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.10.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enriquez R., Frösner G. G., Hochstein-Mintzel V., Riedemann S., Reinhardt G. Accumulation and persistence of hepatitis A virus in mussels. J Med Virol. 1992 Jul;37(3):174–179. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890370305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal S. M., Gerba C. P., Melnick J. L. Human enteroviruses in oysters and their overlying waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):572–581. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.572-581.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K. H., Hollinger F. B., Noonan C. A., Yoffe B. Simultaneous detection of HBV-specific antigens and DNA in paraffin-embedded liver tissue by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization using a digoxigenin-labeled probe. J Virol Methods. 1992 Apr;37(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(92)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Estes M. K., Metcalf T. G., Melnick J. L. Detection of hepatitis A virus in seeded estuarine samples by hybridization with cDNA probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):711–717. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.711-717.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Garland S. M., Lehmann N. I., Pringle R. C., Gust I. D. Solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis A virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):277–282. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.277-282.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen L. R., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H., Wagner J. A. Detection of hepatitis A antigen by immunofluorescence. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):524–530. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.524-530.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf T. G., Moulton E., Eckerson D. Improved method and test strategy for recovery of enteric viruses from shellfish. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):141–152. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.141-152.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. L., Guzewich J. J., Hanrahan J. P., Stricof R., Shayegani M., Deibel R., Grabau J. C., Nowak N. A., Herrmann J. E., Cukor G. Widespread outbreaks of clam- and oyster-associated gastroenteritis. Role of Norwalk virus. N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 13;314(11):678–681. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603133141103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasser A. M., Metcalf T. G. Production of cytopathology in FRhK-4 cells by BS-C-1-passaged hepatitis A virus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2967–2971. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2967-2971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. H., Khanna B., Nainan O. V., Margolis H. S. Epidemiologic patterns of wild-type hepatitis A virus determined by genetic variation. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):286–292. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tecott L. H., Barchas J. D., Eberwine J. H. In situ transcription: specific synthesis of complementary DNA in fixed tissue sections. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1661–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.2454508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Xu X. A new method of RNA preparation for detection of hepatitis A virus in environmental samples by the polymerase chain reaction. J Virol Methods. 1993 Jun;43(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(93)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y. J., Estes M. K., Jiang X., Metcalf T. G. Concentration and detection of hepatitis A virus and rotavirus from shellfish by hybridization tests. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Oct;57(10):2963–2968. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.10.2963-2968.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]