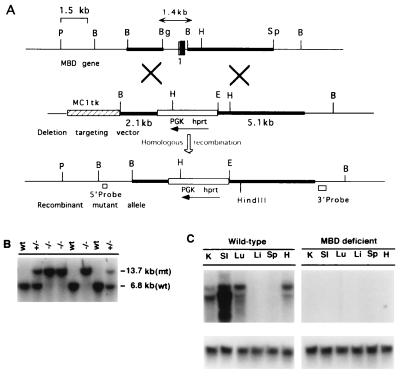
Figure 1.
Targeting strategy for homologous recombination at the MBD locus. (A) Partial restriction maps of the endogenous MBD gene, deletion targeting vector, and the recombinant mutant allele are shown. Coding sequences and introns that are replaced by homologous recombination are indicated by the following: vertical open box, noncoding exon of type I MBD RNA; vertical hatched box, common splice site necessary for all MBD RNAs; vertical solid box, part of the coding exon 1 containing the initiation site ATG and the introns (thin lines). Solid horizontal boxes represent the 5′ and 3′ arms. A phosphoglycerate kinase-hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase expression cassette was used as the positive selectable marker, and an MC1tk expression cassette was used as a negative selectable marker as shown (31). B, BamHI; Bg, BglII; E, EcoRI; H, HindIII; P, PstI; Sp, SphI. (B) Southern blot analysis of BamHI-digested tail DNA; hybridization was performed using a 3′ external probe. wt, wild-type; +/−, heterozygote, −/−, homozygote. (C) Northern blot analysis of total RNA from various tissues of wild-type and MBD-deficient mice. The blots were hybridized using a 620-bp 32P-labeled mouse MBD cDNA probe corresponding to bases +610 to +1230 of the mouse MBD cDNA (28). The blot was stripped and reprobed with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNA to verify equal loading in all lanes.