Abstract
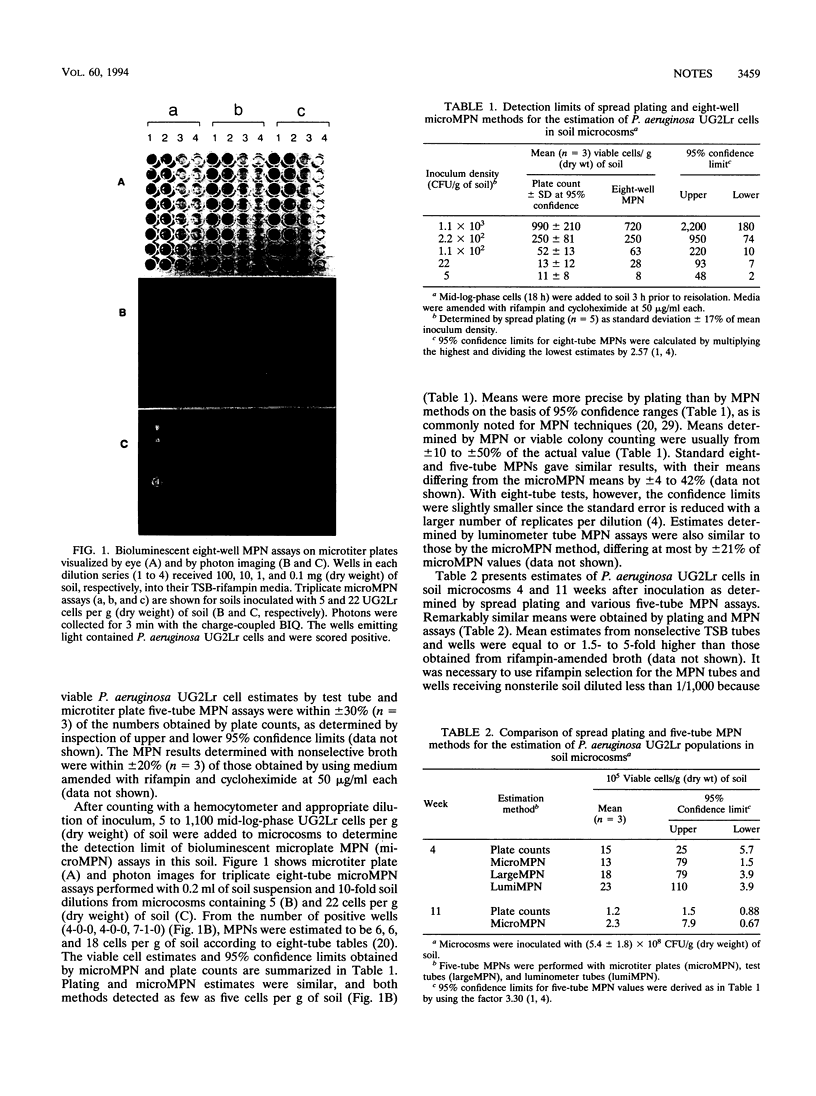
Bioluminescence measured with a luminometer and charge-coupled device was an effective marker in most-probable-number assays for luxAB-marked Pseudomonas aeruginosa UG2Lr in soil. Most-probable-number assays with microtiter plate wells and luminometer tubes gave estimates for UG2Lr that were similar to viable colony counts. Both methods detected five cells per g of soil.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COCHRAN W. G. Estimation of bacterial densities by means of the "most probable number". Biometrics. 1950 Jun;6(2):105–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A., Tirabasso P. A., Grifo A. P., Jr Most-probable-number procedures for enumerating ruminal bacteria, including the simultaneous estimation of total and cellulolytic numbers in one medium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2789–2792. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2789-2792.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemming C. A., Leung K. T., Lee H., Trevors J. T., Greer C. W. Survival of lux-lac-marked biosurfactant-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa UG2L in soil monitored by nonselective plating and PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 May;60(5):1606–1613. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.5.1606-1613.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson J. K., Bezdicek D. F., Brockman F. J., Li S. W. Enumeration of Tn5 mutant bacteria in soil by using a most- probable-number-DNA hybridization procedure and antibiotic resistance. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):446–453. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.446-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitzer A., Webb O. F., Thonnard J. E., Sayler G. S. Specific and quantitative assessment of naphthalene and salicylate bioavailability by using a bioluminescent catabolic reporter bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1839–1846. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1839-1846.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill P. J., Rees C. E., Winson M. K., Stewart G. S. The application of lux genes. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1993 Feb;17(Pt 1):3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson L., Comeau Y., Brousseau R., Samson R., Greer C. Construction and application of chromosomally integrated lac-lux gene markers to monitor the fate of a 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degrading bacterium in contaminated soils. Microb Releases. 1993 Mar;1(4):209–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuko M., Hosoi S., Hayakawa T. A novel method for detection and counting of single bacteria in a wide field using an ultra-high-sensitivity TV camera without a microscope. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jul 1;65(3):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A. Molecular biology of bacterial bioluminescence. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):123–142. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.123-142.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser J. I. Molecular marker systems for detection of genetically engineered micro-organisms in the environment. Microbiology. 1994 Jan;140(Pt 1):5–17. doi: 10.1099/13500872-140-1-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattray E. A., Prosser J. I., Killham K., Glover L. A. Luminescence-based nonextractive technique for in situ detection of Escherichia coli in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3368–3374. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3368-3374.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe R., Todd R., Waide J. Microtechnique for most-probable-number analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):675–680. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.675-680.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russek E., Colwell R. R. Computation of most probable numbers. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1646–1650. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1646-1650.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selifonova O., Burlage R., Barkay T. Bioluminescent sensors for detection of bioavailable Hg(II) in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Sep;59(9):3083–3090. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.9.3083-3090.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. J., Dane F., Geiger D., Kloepper J. W. Use of bioluminescence for detection of genetically engineered microorganisms released into the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):267–273. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.267-273.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silcock D. J., Waterhouse R. N., Glover L. A., Prosser J. I., Killham K. Detection of a single genetically modified bacterial cell in soil by using charge coupled device-enhanced microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Aug;58(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.8.2444-2448.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. I., Couture P., Brauer M., Lee H., Trevors J. T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa UG2 rhamnolipid biosurfactants: structural characterization and their use in removing hydrophobic compounds from soil. Can J Microbiol. 1993 Nov;39(11):1071–1078. doi: 10.1139/m93-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. S., Fung D. Y. Five-tube most-probable-number method using the Fung-Yu tube for enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes in restructured meat products during refrigerated storage. Int J Food Microbiol. 1993 Apr;18(2):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(93)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weger L. A., Dunbar P., Mahafee W. F., Lugtenberg B. J., Sayler G. S. Use of Bioluminescence Markers To Detect Pseudomonas spp. in the Rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Dec;57(12):3641–3644. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3641-3644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]