Abstract
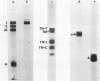
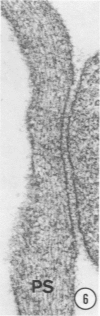
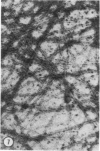
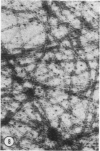
A protein (molecular weight, approximately 250,000) with actin-binding properties has been isolated from human platelets. Addition of the actin-binding protein (ABP) to semiviscous solutions of purified actin containing troponin-tropomyosin (TM-TP) complex resulted in formation of viscous gels consisting of randomly associated actin TM-TP filaments. alpha-Actinin (alphaA), a muscle protein recently detected in platelets, also induced random cross-linking of dissociated actin into gels. Sequential addition of ABP and alphaA resulted in gels consisting of parallel associated actin TM-TP filaments in bundles, suggesting a cooperative interaction. Cytochalasin B (CB) had no apparent effect on the cross-linking of randomly associated actin TM-TP filaments induced by either protein alone but prevented development of bundles of parallel filaments when ABP and alphaA were added sequentially. In addition, CB disrupted the bundles of parallel associated actin TM-TP filaments when added to gels already formed by the dual action of ABP and alphaA and caused simultaneous release of alphaA from the complexes to the supernatant. The findings suggest that platelet ABP and alphaA may induce actin filaments to form the parallel associations observed in platelet pseudopods.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BETTEX-GALLAND M., LUESCHER E. F. Extraction of an actomyosin-like protein from human thrombocytes. Nature. 1959 Jul 25;184(Suppl 5):276–277. doi: 10.1038/184276b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettex-Galland M., Lüscher E. F. Thrombosthenin, the contractile protein from blood platelets and its relation to other contractile proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1965;20:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60387-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Stossel T. P. Interactions of actin, myosin, and an actin-binding protein of chronic myelogenous leukemia leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):964–976. doi: 10.1172/JCI108373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Cohen C. A tropomyosin-like protein from human platelets. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 21;68(2):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Stossel T. P. Isolation and properties of actin, myosin, and a new actinbinding protein in rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5696–5705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markey F., Lindberg U., Eriksson L. Human platelets contain profilin, a potential regulator of actin polymerisability. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 1;88(1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80610-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A. Biochemical and structural studies of actomyosin-like proteins from non-muscle cells. II. Purification, properties, and membrane association of actin from amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):6013–6020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Hartwig J. H. Interactions between actin, myosin, and an actin-binding protein from rabbit alveolar macrophages. Alveolar macrophage myosin Mg-2+-adenosine triphosphatase requires a cofactor for activation by actin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5706–5712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Hartwig J. H. Interactions of actin, myosin, and a new actin-binding protein of rabbit pulmonary macrophages. II. Role in cytoplasmic movement and phagocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):602–619. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Goll D. E., Singh I., Allen R. E., Robson R. M., Stromer M. H. Some properties of purified skeletal muscle alpha-actinin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6860–6870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Fine structural alterations induced in platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):604–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Rao G. H., Gerrard J. M. Effects of the lonophore A23187 on blood platelets I. Influence on aggregation and secretion. Am J Pathol. 1974 Nov;77(2):135–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]