FIG. 2.
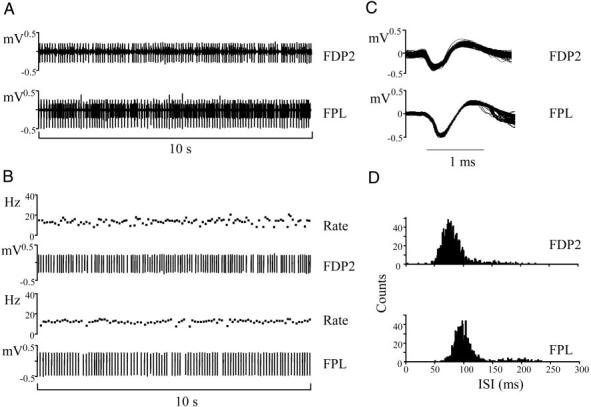
Motor-unit activity during object hold. A: raw electromyographic (EMG) data from the index finger compartment of FDP (FDP2; top) and a thumb flexor (FPL; bottom). B: motor units discriminated from each raw EMG trace and their respective instantaneous firing rates (bottom and top, respectively). C: the action potentials of the discriminated motor units (1347 and 1144 from FDP2 and FPL EMG records, respectively). D: the interspike interval (ISI) distributions of each motor unit. The data shown in A and B are from a smaller recording period than the entire duration of the object hold trial (∼4 min). All traces are from the same subject (subject 3).
