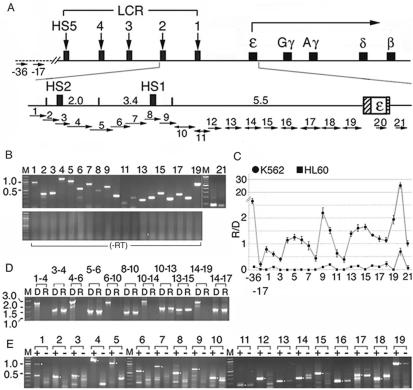
Figure 1.
The ε-globin gene locus was transcribed into short, overlapping, polyadenylated RNAs in the direction from the HS2 enhancer to the globin gene. (A) Top: the human β−globin gene locus. Rectangles with vertical arrows: DNase I hypersensitive sites HS1-5 defining the LCR; squares: the globin genes; angled arrow: transcription direction of the globin genes. Bottom: the enlarged ε-globin gene locus. Numbers: sizes in kb of Hind III fragments spanning HS2, HS1 and the intervening DNA; hatched and horizontally-striped bars: the ε-globin promoter and the polyadenylation signal. Short horizontal arrows: locations of overlapping primer pairs 1–12 and non-overlapping primer pairs 12–21. Direction of the arrows: transcriptional direction of the intergenic RNAs determined in Figure 1E; arrows with bi-directional arrowheads: RNAs transcribed in both sense and anti-sense directions; sizes of arrowheads: relative abundance of the sense and anti-sense RNAs. −17 and −36: Two control primer pairs located at 17 and 36 kb upstream of the HS2 site in DNA outside of the globin gene locus, marked by the dotted line. (B) Upper panel: RT–PCR bands generated by K562 total cellular RNAs that were reversely transcribed with an oligo dT primer (15) and amplified with primer pairs 1–21 (lanes 1–21). Lower panel: blank lanes amplified with the respective primer pairs from the RNA sample without reverse transcription to ensure absence of DNA contamination. M: 100 bp size markers. (C) Average levels of the intergenic RNAs in K562 and non-erythroid HL60 cells. R/D: the cycle number at the crossing over point of the RT–PCR products (Rcop) subtracted from those of the DNA PCR products amplified by the same primer pair in real-time PCR (Dcop), to correct for different amplification efficiencies of the primer pairs. The R/D ratios were further normalized with respect to the R/D value of β-actin for comparison of the transcription profiles in K562 and HL60 cells. The average normalized values of 2Dcop–Rcop from two independent experiments were presented on the Y-axis. (D) The polyadenylated, intergenic RNAs were <3 kb in length. Lanes 1–4, D and R lanes: K562 genomic DNA and cDNAs synthesized from cellular RNAs as in B and amplified with the forward primer of primer pair 1 and the reverse primer of primer pair 4; lanes 3–4: DNA and cDNA templates amplified with the forward primer of primer pair 3 and the reverse primer of primer pair 4. The remainder D and R lanes were amplified similarly with overlapping primer pairs as marked. M: size markers in kilobase. (E) Directional RT–PCR (15). + and –lanes: RT–PCR bands generated from the sense and the anti-sense RNAs in total K562 cellular RNAs. Sense RNAs were reversely transcribed into cDNAs with the reverse primers and anti-sense RNAs with the forward primers of primer pairs 1–19 followed by PCR with the respective primer pairs 1–19. Lanes 2, 3, 8 and 12 were amplified by 40 PCR cycles; other lanes, 36 PCR cycles. Dots in the margins: anticipated sizes of the RT–PCR products.