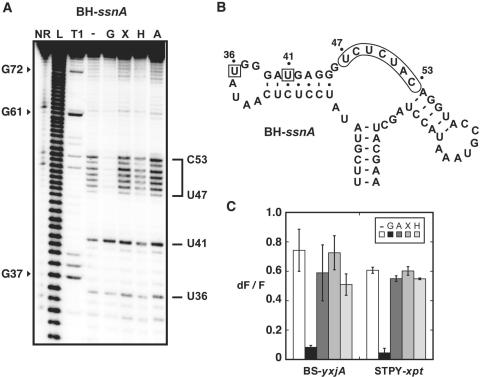
Figure 3.
Natural structural variations do not alter aptamer specificity. (A) In-line probing assays of the BH-ssnA variant in the presence of guanine (G), xanthine (X), hypoxanthine (H) and adenine (A). Radioactively [5′-32P]-labeled molecules were incubated for 72 h at room temperature in absence of ligand (−) or in presence of 1 µM ligand to allow spontaneous backbone scissions. Sites of substantial cleavage are assigned on the right. Lanes NR, L and T1 correspond to molecules that were non-reacted or that were partially digested by alkali, or by RNase T1, respectively. Guanines are indicated on the left as molecular weight markers. (B) Sequence and secondary structure of the BH-ssnA variant and summary of in-line probing results. Indicated positions represent cleavage sites. The core region undergoing a structural reorganization in presence of guanine is indicated while squares denote a constant scission. (C) Competition assays for BS-yxjA and STPY-xpt variants. In each experiment, aptamers were incubated in presence of 2AP and an excess of guanine (G), adenine (A), xanthine (X) and hypoxanthine (H). For each measurement, the normalized 2AP fluorescence intensity is calculated and is inversely proportional to the 2AP displacement performed by the competing metabolite. For each aptamer, a control experiment was performed without competing metabolite (−). Each experiment was performed three times and the average as well as the SD are shown.