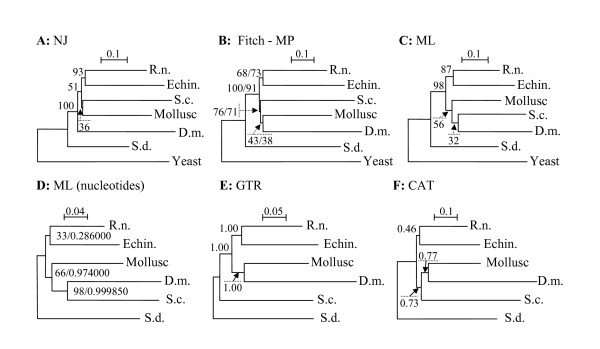
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic trees of the selected ribosomal proteins sequences (see Table 2 and Methods). The trees A, B and C were obtained using respectively Neighbor Joining (NJ), Fitch, Maximum Parsimony (MP), and Maximum Likehood (ML) methods on an amino acid dataset. The trees constructed using Fitch and MP methods have a similar topology. In D, the ML tree using the first two codon positions and the model selected by MrAIC, GTRIG, ML estimated base frequency, a gamma (2) distribution for site substitution rates, and an estimated proportion of invariant sites. Similar topologies were obtained with ML using codon models and with a non homogeneous non stationary ML method allowing G+C equilibrium frequency to vary (see text). Trees E and F were obtained using respectively the GTR model with a MCMC bayesian method and the CAT mixture model on an amino acid dataset. Numbers indicate bootstrap values or branch support; in tree B, MP and Fitch values are respectively at the left and at the right, in tree D, after the slash, the aLRT (actually the minimum of the CHI2-based parametric and non parametric aLRT estimated value). Abbreviations: D.m., D. melanogaster; Echino., Echinoderm; R.n., R. norvegicus; S.c., S. cephaloptera; S.d., S. domuncula; Yeast, S. cerevisiae.