Figure 2.
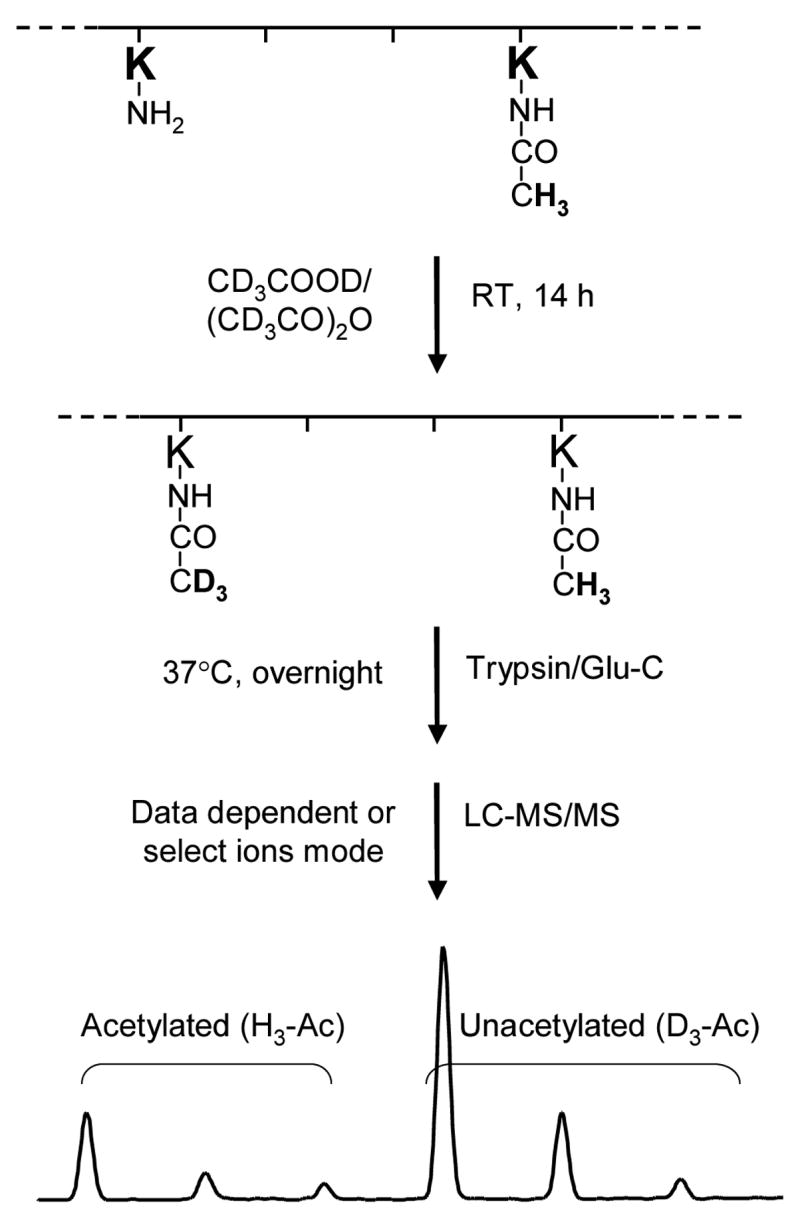
An outline of the experimental approach employed to quantify the in-vitro and in-vivo acetylation of HMGA1a and HMGA1b. HMGA1 proteins were treated with deuterated acetic anhydride and deuterated acetic acid for 14 h. As a result, each of the unacetylated lysine residues was conjugated with a deuterated acetyl group. Digesting the proteins with trypsin or Glu-C produced the desired peptides, in which the acetylated lysine residue (either endogenously acetylated in PC-3 cells or in-vitro acetylated by p300 or PCAF) was tagged with a protiated acetyl moiety (H3-Ac) and the unacetylated lysine residue was attached with a deuterated acetyl group (D3-Ac). Since the mass difference between H3-Ac and D3-Ac is 3 Da, the acetylation level can be determined from the ratio of the abundance of ions bearing H3-Ac over the sum of those bearing H3-Ac and D3-Ac.
