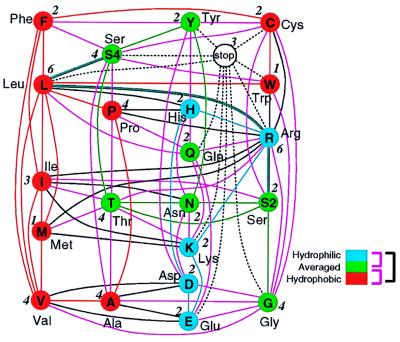
Figure 1.
Graph representation of SGC with the polarity of amino acids. The letters in the nodes are one-letter abbreviations of amino acids, except for S2 and S4. Each node in the graph is defined as a set of codons that code the same phenotype, where the codons in the set can change to any other in the same set through successive transitions with a single base mutation connected by a line called an edge, if the single base mutant of a codon in one node belongs to the other node; then, 20 phenotypes except for Ser correspond in one to 20 nodes of the graph. By the definition of the node, the set of codons coding Ser is divided into two nodes S2 = {AGU, AGC} and S4 = {UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG}. Red denotes a hydrophilic, green denotes an averaged (neutral), and blue denotes a hydrophobic amino acid. Connections between the amino acids are classified with colored edges, e.g., a purple edge represents a connection between a neutral and either a hydrophobic or hydrophilic amino acid. The numbers give the sizes of the nodes. The number of vertices with size 1, 2; size 2, 10; size 3, 2; size 4, 6; size 5, 0; and size 6, 2.