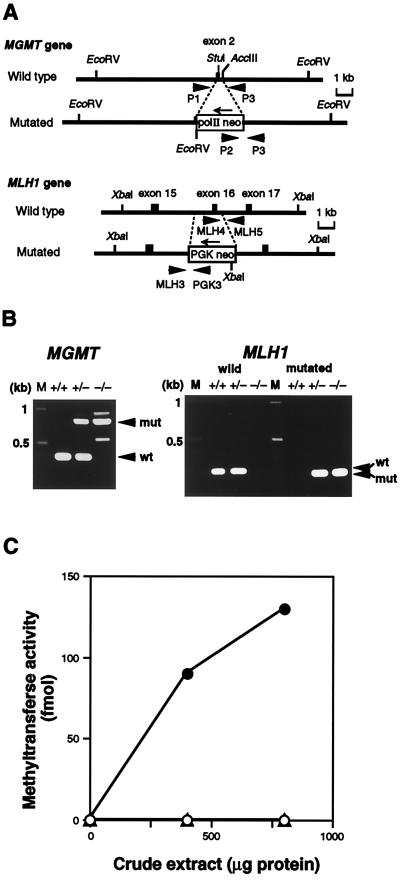
Figure 1.
Targeted disruption of the mouse MGMT and MLH1 genes. (A) Schematic representation of targetings of the MGMT and MLH1 genes. Structures of parts of the wild-type (Upper) and the mutated sequences resulting from homologous recombination (Lower) are shown. Exons are shown as solid boxes. Thick arrows indicate PCR primers for genotyping of mice, and thin arrows represent the directions of transcription of the inserted cassettes. Appropriate restriction sites are shown. (B) Genotyping of progenies. To detect wild-type and mutated MGMT alleles (Left), PCR was done using three primers: P1, P2, and P3. The lengths of PCR products for wild-type (wt) and mutated (mut) alleles were 380 bp and 800 bp, respectively. For analyses of the MLH1 locus (Right), two sets of primers, MLH4-MLH5 (for wild type) and MLH3-PGK3 (for mutated allele), were used. The former gave a 260-bp PCR product (wt), and the latter a 220-bp one (mut). M, DNA size marker. (C) O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase activity. Crude extracts were prepared from thymus, and the extracts were incubated with [3H]MNU-treated calf thymus DNA. (○), MGMT−/− MLH1+/+; (▵), MGMT−/− MLH1−/−; (•), MGMT+/+ MLH1+/+.