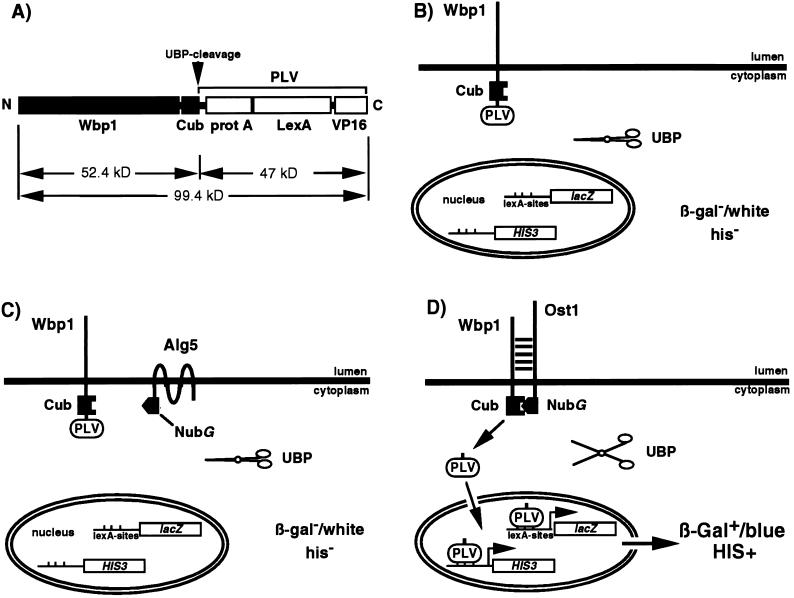
Figure 2.
Design of Wbp1-Cub-PLV fusion protein and the principle of detection of the interaction. (A) The structure of the mature Wbp1-Cub-PLV fusion protein. Cleavage by the UBP(s) occurs at the C terminus of Cub, cleaving the Wbp1-Cub-PLV fusion protein of ≈100 kDa into Wbp1-Cub (52 kDa) and PLV (47 kDa). (B) Expression of PLV as a fusion to the ER membrane protein Wbp1p prevents the transcription factor from gene activation in the nucleus. Cleavage of Wbp1-Cub-PLV by UBP does not occur (solid scissors) in the absence of Nub, the cells are white in the presence of X-Gal and are His auxotrophs. (C) Coexpression of Wbp1-Cub-PLV with the noninteracting NubG-Alg5p does not lead to formation of the split-ubiquitin heterodimer, nor cleavage by UBP (solid scissors) and gene activation. (D) Interaction between Wbp1 and Ost1 results in formation of the split-ubiquitin heterodimer. The heterodimer is recognized and cleaved by the UBP (open scissors), liberating PLV. PLV can enter the nucleus by diffusion and bind to the LexA-binding sites leading to activation of transcription of the lacZ and HIS3 reporter genes. This results in blue cells in the presence of X-Gal and growth of the cells on agar plates lacking histidine.