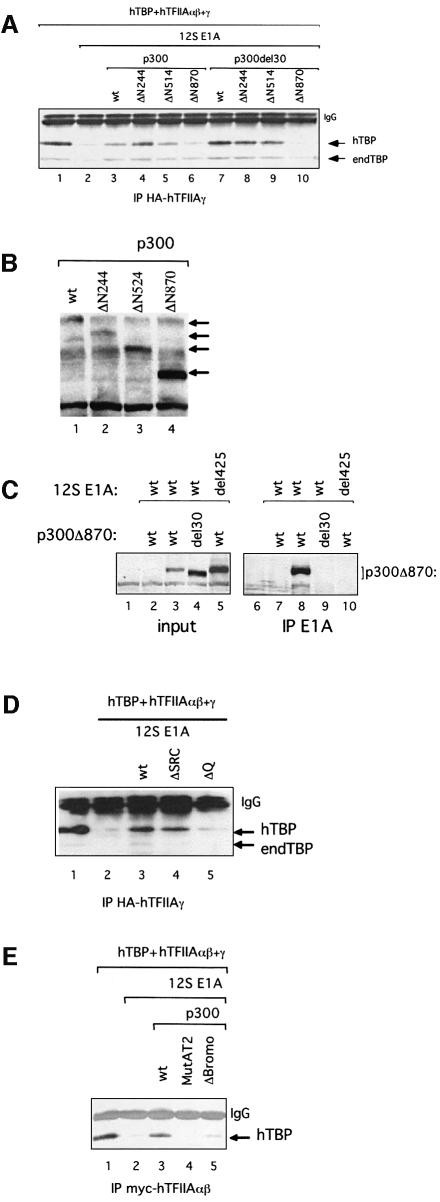
Fig. 4. Domains of p300 required for TAC formation in P19 EC cells. (A) Effect of the N-terminal truncations of p300 on TAC formation in the presence of 12S E1A in P19 EC cells. Extracts from P19 EC cells transfected with expression plasmids encoding hTBP and hTFIIAαβ + γ, in the presence or absence of 12S E1A and Myc-tagged p300 (wt and del30, full-length or N-terminal truncations), were subjected to immunoprecipitation using the HA antibody. Peptide elution was followed by immunoblotting using SL39. (B) Expression of p300 in P19 EC cells. Extracts from P19 EC cells transfected with expression plasmids encoding Myc-tagged p300 (as in A) were subjected to immunoblotting using an antibody against p300 (Myc). (C) E1A interacts with the CH3 domain of p300 in an N-terminal-dependent manner. Extracts from P19 EC cells transfected with plasmids expressing12S E1A (wild-type or del4–25) and Myc-tagged p300 ΔN870 (wt or del30) were subjected to immunoprecipitation using the anti-E1A antibody M73. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting as in (B). The input represents one-tenth of the samples analyzed for immunoprecipitation. (D) Effect of C-terminal mutants of p300 on TAC formation in the presence of 12S E1A in P19 EC cells. Extracts from P19 EC cells transfected with expression plasmids encoding hTBP and hTFIIAαβ + γ, in the presence or absence of 12S E1A and Myc-tagged p300 (wt, ΔSRC or ΔQ), were subjected to immunoprecipitation and western blotting as in (A). (E) The HAT domain and bromodomain of p300 are required for TAC formation in the presence of 12S E1A in P19 EC cells. Extracts from P19 EC cells transfected with expression plasmids encoding hTBP and hTFIIAαβ + γ, in the presence or absence of 12S E1A and Myc-tagged p300 (wt or mutants), were subjected to immunoprecipitation using the Myc antibody and western blot analysis as in (A). endTBP = endogenous TBP.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.