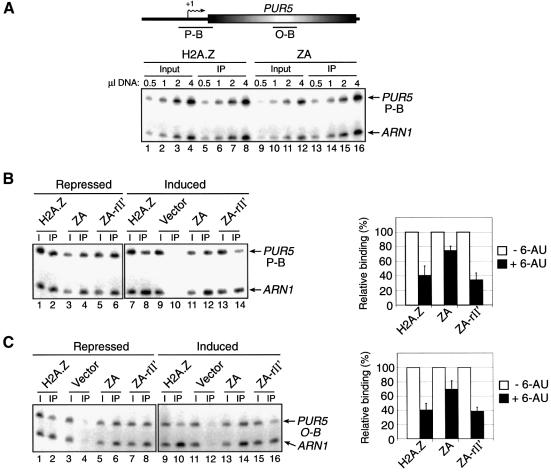
Fig. 4. Binding of H2A.Z derivatives at the PUR5 gene. ChIP experiments were performed using anti-HA antibodies to monitor the binding of H2A.Z, ZA and ZA-rII′ to PUR5 under repressed (–6-AU) or induced (+6-AU) conditions. All PCRs contain ARN1 primers used here as an internal control to normalize signals for each lane. (A) Top: representation of the PUR5 locus. Transcription start site (arrows with +1), open reading frame (open shaded rectangle) and regions amplified by PCR (black bars) are represented. Bottom: PCR titration of input (lanes 1–4 and 9–12) and immunoprecipitated material (lanes 5–8 and 13–16) for H2A.Z (lanes 1–8) and ZA (lanes 9–16) at the PUR5 promoter. (B) ChIP analysis of the binding of H2A.Z derivatives at the PUR5 promoter. Binding of the derivatives under repressed (–6-AU, lanes 1–6) and induced (+6-AU, lanes 7–14) conditions (left panel). The right part of the figure depicts a quantification of that experiment. Binding of each H2A.Z derivative under repressed conditions is normalized to 100%. (C) Same experiment as in (B) with the exception that the PUR5 region analyzed was in the open reading frame.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.